Introduction
A voltage amplifier is an electronic device that takes an input signal and improves its strength without changing the shape. It can handle small or large signal sizes depending on the function and configuration, and this article provides a brief look at how it depends on the relationship between supply, load, and current. Such amplifiers are widely used in communications, broadcasting, and audio equipment where reliable operation is the main need.
The classification of amplifiers comes in different forms, from Op-Amps to power stages, with methods based on signal processing and physical kinds of design. A range of applications exists in wireless systems where forms of configuration can increase the power output. Their function depends on how the amplifier handles different loads, and this relationship is what provides the true value of classification in both small and large-signal designs.
What is a voltage amplifier?
A voltage amplifier is a special type of amplifier that creates a higher output than the input signal, making it suitable for longer wire transmission where power and clarity are necessary. It is used in electronics to make audio signals clearer, sharper images, and accurate sensor readings, giving the desired result without changing the character of the signal significantly. This helps in many different areas where electrical devices and controls need better readings.
While it does not directly supply motors or heavy devices, it improves what is available by increasing the amount of power coming through a circuit. Generally, such amplifiers help by making weak signals stronger and more useful for electronics, ensuring the result is stable and reliable. The ability to give clearer outputs depends on how the design handles different readings and available input, which makes it widely known in practical applications. You can also read about phototransistor.
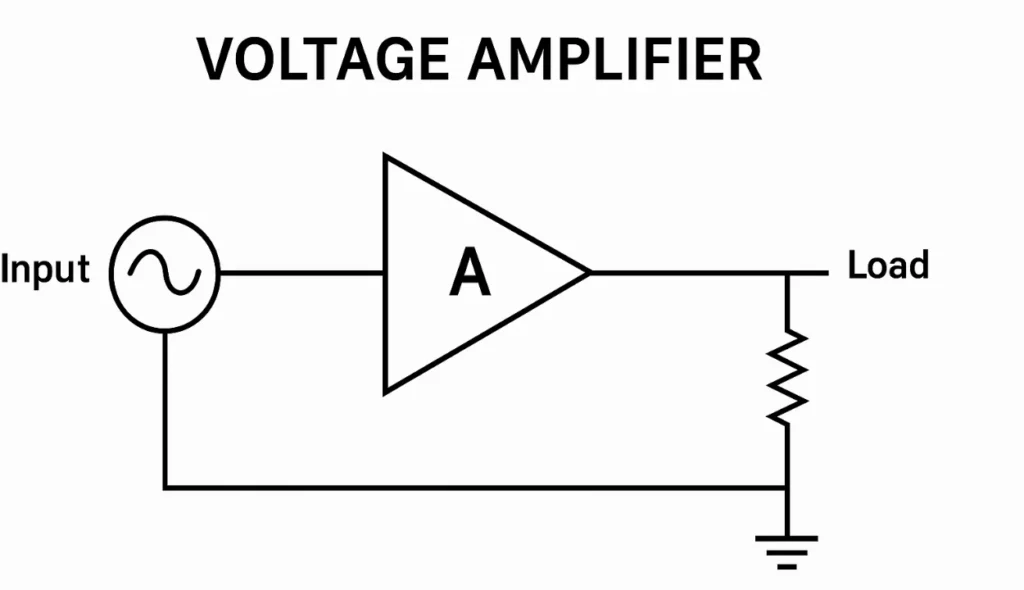
How Voltage Gain Works in Amplifiers?
The amplification in a voltage amplifier mainly depends on the ratio of output (o/p) to input (i/p), where Vout and Vin are the key values in the formula for Av. This unit is known for its design to enhance the signal level and reach the maximum achievable gain, making it highly useful in practical circuit applications. The value of this ratio is often treated as an equivalent measure that shows how the amplifiers improve performance.
These types of small-signal amplifiers usually draw extremely small amounts of power from a connected load, but the signal magnitude can still be raised effectively. The provided design ensures that the amplification is balanced, with the raised value making the system more reliable. In this way, amplifiers provide a stable gain while handling different circuit conditions to achieve the desired result. You can also read about local oscillator.
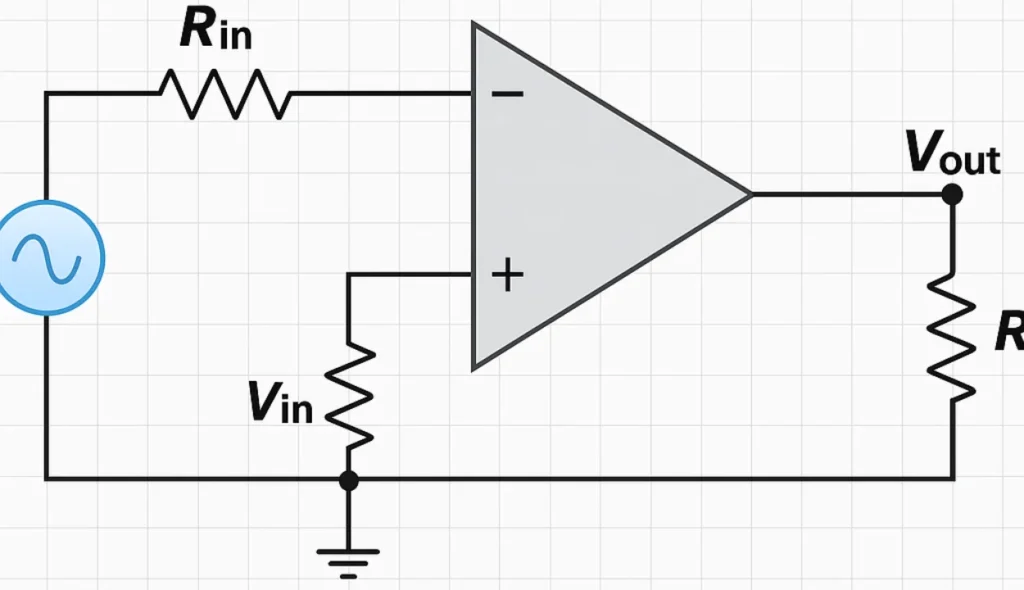
Voltage Amplifier Circuit
The design of an amplifier circuit is often simple when basic electronic components are called for. A voltage difference amplifier can amplify two voltages, giving a changing output that can be read and analyzed as needed. In practice, the shown layout handles input signal flow and provides an output through a voltage-controlled source.
The impedance of an ideal amplifier must be high at the input and low at the output, with Rin, Rs, Vin, and Vs adjusted to balance the circuit. A load like RL and its resistance with Rout influence the Vout, while formulas such as AvVin, Vout/Vin, or Vout/Vs define the gain (Av). To be accurate, it should include infinite input resistance, zero output resistance, and stay proportional with a constant proportionality factor that is independent of source magnitudes and resistances.
Difference between Voltage Amplifier and Power Amplifier
From my own work in audio equipment and wireless communication systems, I have often discussed the differences between a voltage amplifier and a power amplifier. Each is designed for an exclusive role: one to enhance amplitude of the input signal, the other to drive high-power loads like loudspeakers. Both are used frequently across scientific, industrial, and RF applications, but their gain, current, and heat dissipation vary greatly.
| Point | Voltage Amplifier | Power Amplifier |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Designed to amplify voltage of input signal | Designed to provide power gain |
| 2 | Focus on small amplitude and exclusive signal work | Focus on driving large high-power loads |
| 3 | Often called a small amplifier | Known as a large amplifier |
| 4 | Transistor base is thin, handles small current | Transistor base is thicker, handles huge currents |
| 5 | Uses low-power or medium transistor with small physical size | Uses high-power transistor with large physical size |
| 6 | Collector current value ≈ 1 mA | Collector current value ≈ 100 mA |
| 7 | AC o/p power is low | AC o/p power is high |
| 8 | Gain in the circuit is low | Gain in the circuit is high |
| 9 | Usually coupled with RC | Usually coupled with transformer |
| 10 | Heat dissipation is low | Heat dissipation is high |
| 11 | Used frequently in audio equipment to enhance signal without significantly increasing power | Provides strong output for wireless communication, scientific, and industrial applications |
Difference between Voltage Amplifier and Power Amplifier
Both are known for handling signals, but they work on different principles. A voltage amplifier is used to enhance the input signal while maintaining a stable current, whereas a power amplifier focuses on amplifying large output with higher gain.
| Point | Voltage Amplifier | Power Amplifier |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Works with input voltage and less current | Works with input current and produces larger output |
| 2 | Gain is high for voltage | Gain is high for current |
| 3 | Impedance: high i/p and low output | Impedance: low i/p and high output |
| 4 | Best for medium range electrical signals | Best for large amplifying signals |
| 5 | Maintaining stable operation, suited for precise electronic devices | Known for driving different loads that need high output |
Practical Applications of Voltage Amplifiers
When we look at real-world applications of voltage amplifiers, they are frequently seen across many electronic devices. Their role is to enhance the amplitude of a signal so that the output voltage is strong enough for different tasks, from everyday audio needs to complex communication systems. I’ve worked with circuits where even a weak input had to be lifted to its maximum level for proper use.
Used in speakers and audio equipment to strengthen signal quality.
Applied in radios to amplify weak signals received by an antenna.
Helpful in wireless communication and broadcasting for long-distance transmission.
Works in impedance matching and switching circuit design.
Essential for long wire circuit connections where voltage needs to be maintained.
Supports a variety of applications in both home and industrial equipment.
Conclusion
In simple terms, a voltage amplifier is one of the most important building blocks in electronics, ensuring that weak signals are strengthened without losing quality. From audio equipment and radios to wireless communication and industrial applications, it plays a vital role in reliable performance. Its ability to provide stable gain, manage different loads, and deliver clear outputs makes it highly valuable in modern systems. With designs ranging from op-amps to advanced circuits, voltage amplifiers continue to be used across a wide range of technologies. Whether in small devices or large applications, they remain essential for maintaining efficiency, clarity, and signal strength.
