Introduction
Three-phase power systems are the backbone of modern industry. They efficiently transmit power over long distances and balance it across three conductors. Three-phase power is transmitted and distributed using two connection types: star and delta.
The difference between star and delta connections lies in their configuration and performance. A star configuration has one common neutral point. This often makes it suitable for power distribution systems that require different voltage levels. It provides flexibility in phase voltage and line voltage, offering a reliable setup for distribution in low-voltage applications. In contrast, the delta configuration forms a closed loop, lacking a neutral wire. This arrangement is generally preferred in power transmission and industrial motor connections for its ability to handle high power loads.
This article explores these differences. It outlines how each connection type affects voltage, current, and system efficiency. Knowing these variations is crucial. It helps in selecting the right three-phase power setup for both residential and industrial electrical systems.
What are star and delta connections?
In three-phase AC systems, the star (or wye) and delta configurations are two primary ways of connecting electrical circuits. These configurations set the phase and line voltage relationships. They affect the performance, efficiency, and safety of AC power systems.
Star Connection (Wye Configuration)
In a star connection, three winding terminals are connected at a common neutral point, creating a Y-shaped circuit. This setup includes four wires: three phase wires and one neutral wire. Key characteristics include:
Phase voltage is lower than line voltage by a factor of √3.
It’s suitable for long-distance power transmission and distribution systems. It has lower insulation requirements and a neutral line.
Used in low-voltage applications and systems needing different voltages, such as in residential and commercial electrical systems.
Delta Connection
In a delta connection, the end of each winding is connected to the start of the next, forming a closed-loop triangular circuit. Characteristics of the delta configuration include:
Line voltage is equal to phase voltage, providing a higher power transfer capability.
A lack of a neutral wire makes it ideal for industrial motors and heavy-duty equipment. They need stable, high-power output.
Commonly used in power transmission networks where high power loads and efficiency are essential.
Importance in AC Power Transmission and Distribution Systems
The choice between star and delta connections affects power transmission. It impacts efficiency, safety, and suitability for applications. Star configurations are versatile in adjusting phase voltages. They are preferred in distribution systems with common, varying voltage levels. Meanwhile, delta configurations ensure stable performance in high-load, continuous power systems. So, they are vital in industrial settings.
Structure and Configuration of Star and Delta Connections
In three-phase AC systems, star and delta connections are common. Each has a unique layout and application. They are foundational to effective power transmission and distribution in electrical systems.
Star Connection
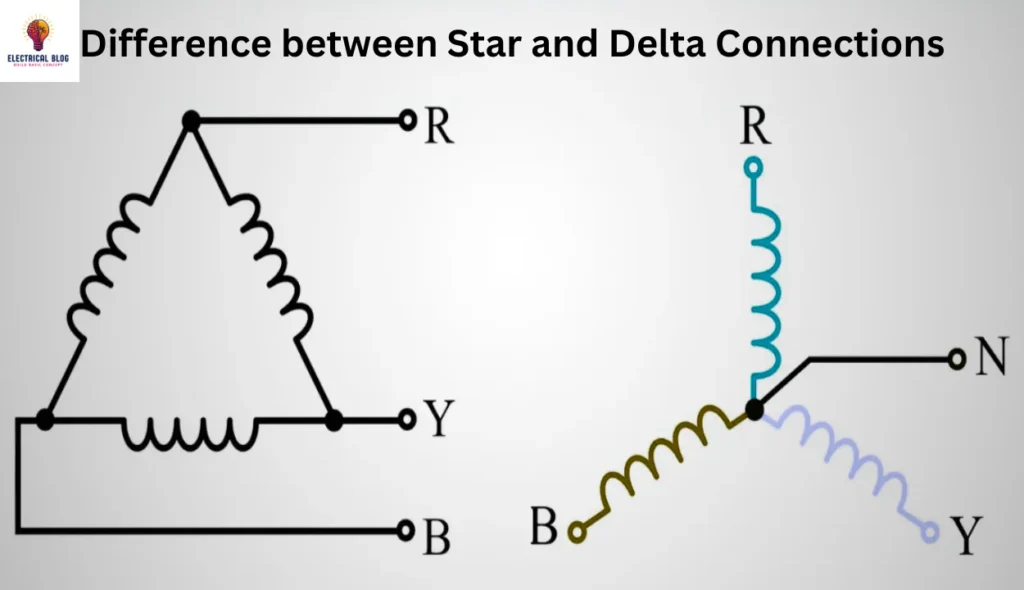
Physical Layout: In a star connection (also known as the wye connection), each of the three phases connects at a common neutral point, forming a ‘Y’ shape. This setup is often shown with three phase wires from each phase. They all converge at a single central point.
Four-Wire System: The star connection utilizes a four-wire system. It has three phase wires and one neutral wire. This setup allows for versatile voltage levels in systems, as phase voltage is lower than line voltage by a factor of √3.
Star connections are common in long-distance power networks. They are needed where variable voltage levels are required. This connection is also common in residential areas and commercial applications where a neutral wire is beneficial for load balancing and safety. Additionally, it is preferred in low-voltage systems due to its reduced insulation requirements.
Delta Connection
Physical Layout: In a delta connection, the three phases are arranged in a closed loop, forming a triangular (delta) shape. Each phase connects to the start of the next, creating a continuous loop with no central neutral point.
Three-Wire System: Unlike the star configuration, the delta connection is a three-wire system with no neutral wire. Here, the line voltage is equal to the phase voltage, making it well suited for applications requiring stable, high-power output.
Common Uses in Industrial Settings and Motor Connections: The delta configuration is popular in industry and for connecting high-power motors. It provides a stable, high-power supply, making it ideal for industrial machinery that demands continuous power with minimal fluctuation. Delta connections are also preferred in transmission systems where efficiency and high-load capacity are essential.
Key Differences Between Star and Delta Connections
Star and Delta connections are key in three-phase systems. Each has unique advantages based on voltage, current, and application needs.
Voltage and Current Characteristics
Star Connection: In a Star connection (or Wye connection), the phase voltage is lower than the line voltage by a factor of √3. It lowers phase currents. This reduces insulation needs and costs for long-distance transmission.
Delta Connection: In a Delta connection, the line current is higher than in a Star connection, as it carries the sum of the phase currents. This configuration provides a stable and higher current output, suitable for systems requiring more power. Delta connections are often preferred in high-load applications like heavy machinery.
Power Transmission vs. Power Distribution
Star Connection: Star connections are better for long-distance power transmission and for systems needing different voltage levels. They have a neutral point. The star configuration is efficient in reducing power loss over long distances, which is crucial in distribution networks.
Delta Connection: Delta connections are common for local power distribution, especially in industry. They are advantageous in situations where a stable and high-current output is needed for powering equipment like motors. The Delta system, with no neutral point, meets some industrial power needs. It helps maintain a constant supply in heavy-load applications.
Efficiency and Torque Output
Delta Connection: Delta connections are more efficient and provide higher torque. They are ideal for heavy machinery and industrial uses that need high power. This higher torque is vital for devices that must handle variable loads. It is especially important for motors and other rotating equipment. They must remain stable despite the changing loads.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Star and Delta Connections
Understanding the benefits and limitations of Star and Delta connections is essential in power systems and motor applications. Each configuration has unique traits. They make it suitable for specific applications, based on power needs and load conditions.
Star Connection Advantages
Lower Current: In a star connection, each phase carries a reduced current compared to a delta connection. This reduces power loss in transmission lines, making it more efficient over long distances.
Less insulation is required: A star connection has a lower phase voltage than the line voltage. So, it needs less insulation for each winding. This cuts costs and makes it ideal for high-voltage applications.
Suitable for Long-Distance Power Transmission: Star connections are widely used for long-distance power transmission. They lower line current and reduce insulation needs, which cuts power losses.
Star Connection Disadvantages
Lower Starting Torque: The star configuration often generates less torque at startup. It is less suitable for heavy-duty applications that require high initial torque. This is a critical factor when choosing motor configurations.
Delta Connection Advantages
Higher Power Output and Torque: A Delta connection provides higher torque and power output because the line voltage is applied directly across each winding. This is ideal for motors requiring high initial torque, such as in heavy machinery.
Suitable for Applications Requiring High Starting Torque: Delta connections are preferred in applications that need a fast startup. So, they are common in industrial settings and for high-inertia loads.
Delta Connection Disadvantages
Higher current leads to greater power loss over long distances: a delta connection has a higher line current. This leads to greater power loss when transmitting power over long distances. This limits its efficiency for transmission use. It’s better for localized power delivery than for long-distance distribution.
Applications of Star and Delta Connections
Star and Delta connections are fundamental configurations in three-phase power systems. Each connection type has specific advantages. They suit different real-world uses in power systems, motor control, and industry.
Star Connection Applications
The star connection is popular in distribution systems. It can handle lower currents and reduce insulation needs. Here are some typical applications:
Residential and Commercial Power Distribution: Star connections are common in residential and commercial power distribution. This setup allows the use of a neutral wire, which provides dual voltages: single-phase for residential use and three-phase for commercial settings.
Long-Distance Power Transmission: The star configuration uses lower current. It minimizes power losses over long distances. This makes it ideal for transmitting electricity from power stations to substations with minimal power loss.
Small Load Applications: For motors and appliances with low power needs, star connections are often preferred. They have lower starting currents. This makes them efficient and cost-effective for smaller devices.
Delta Connection Applications
The Delta connection is known for its high current and load capacity. It is suitable for industrial and heavy machinery applications.
Industrial Power Distribution: Delta connections are common in industry. They provide high power and greater starting torque for machines. The absence of a neutral point allows each phase to carry the full line voltage, which is critical in heavy-duty machinery applications.
Motor Control and High Starting Torque: In motor control, Delta connections are preferred when high starting torque is needed. This is the case in conveyor systems and other heavy-load machines. The Delta configuration provides the necessary initial power surge to start these motors effectively.
Three-Phase Motor Starters: Delta connections are often used in Star-Delta motor starters. These starters first connect the motor in Star to reduce the starting current. Then, they switch to Delta to increase power in normal operation.
Transition from Star to Delta connections and vice versa
The star-delta connection method is a widely used technique in electrical systems, especially in the operation of motors. This technique allows for the switching between star and delta configurations to optimize the performance of motors.
Star to Delta and Delta to Star transformation
We swap out a star-connected network for its corresponding delta-connected network in a star-delta transformation, and vice versa. This technique is especially useful when dealing with different voltage or current values in a system. The star configuration has a neutral point, and each phase of the system is connected to the neutral. In contrast, the delta configuration has no neutral, with the phases connected to form a closed loop. The switch from star to delta (or vice versa) allows systems to adapt to different operational needs, providing flexibility in voltage management and balancing loads.
Explanation of Star-Delta Starters in Motors
The star-delta starter is a type of reduced voltage starter used for motors. It helps reduce the inrush current when a motor starts. Initially, the motor is connected in a star configuration, where the voltage across each winding is lower, reducing the starting current. Once the motor reaches a certain speed, the connection is switched to delta, allowing full voltage to flow through the motor windings, thus enabling it to run at full power.
This method is highly effective for reducing the high starting current, which can be detrimental to electrical equipment and the motor itself.
Advantages of Using Star-Delta Switching for Reducing Starting Currents
Reduced Starting Current: Using a star connection at startup reduces the motor’s voltage. This cuts the starting current to one-third of that in a delta connection.
Cost-Effective: A star-delta starter needs inexpensive components. So, it is a low-cost solution for large motors.
Preventing Damage: Lower starting currents reduce thermal stress on motor windings and other components during startup.
Choosing the Right Connection Type
Choosing the right connection type is key. It ensures the efficiency, safety, and longevity of electrical systems. It involves several key factors. These include the distance, power needs, and application type. Each of these elements plays a crucial role in determining the most appropriate type of connection for a given system.
Factors Influencing the Choice of Connection Type
Distance
The distance between components significantly impacts the choice of the connection type. Longer distances may require thicker cables or special connectors to reduce signal loss, voltage drop, or resistance. In low-voltage uses, short distances may need only basic connectors. Long-distance links might require reinforced or shielded cables.
Power Requirements
Power requirements are another major factor in selecting the right connection. High-power applications often demand connectors that can handle greater currents without overheating. The current rating of connectors and cables should be compatible with the expected load to prevent safety hazards or inefficiency. For instance, in high-power industrial machinery, heavy-duty connectors are necessary to handle the load.
Application Type
The application type affects the connection type. It could be for general electrical, automation, industrial, or commercial use. For sensitive equipment, you might need special connectors. They should have specific insulation ratings or be corrosion-resistant for harsh environments.
Tips for Selecting the Correct Configuration in Design and Implementation
Compatibility with Voltage and Current: Ensure that the connectors and cables are rated for the correct voltage and current capacity. Choosing the right connection type with compatible voltage ratings helps avoid overloading and damage to the system.
Safety and Compliance: Ensure that the chosen connection types meet safety standards and regulations to avoid electrical hazards.
Mechanical Robustness: For apps with mechanical stress, use rugged, secure connectors. Consider connectors that can withstand vibrations, environmental conditions, and wear and tear.
Conclusion
Knowing the differences between star and delta connections is vital for designing and implementing electrical systems. The star connection is used when a neutral point is needed for grounding, or when voltage control is a priority. It reduces phase voltage and improves safety. The delta connection is often chosen for high-power uses. It provides a higher line-to-line voltage. This makes it ideal for heavy machinery and motor loads.
The impact of these differences can be seen in the way they affect the overall system design. A star connection is more stable and safer for low-voltage systems. It is vital where neutral grounding is needed. A delta connection, however, is better for larger loads. It is more efficient in power distribution, especially in industrial settings.
Understanding both connection types is essential for optimizing system performance. The right choice depends on the power needs, the distance between components, and the application type. So, one must carefully assess the system’s needs before choosing the best configuration. Choosing the right connection, whether star or delta, is vital. It ensures reliability, safety, and efficiency in electrical system design.
Read more: Current Carrying Capacity of Aluminium Cable


