Introduction
When I first installed a double pole double throw switch, I was impressed by how easy it was to set up without using a single nut, bolt, or screw. The locking system really stood out — it could lock and unlock the switch directly in a remote cabinet, which saved me time during setup. These electromechanical switches are formed by adding a pole to a SPDT design, making them more flexible in applications that need a double-throw and double-pole setup. From my experience, the overview of how it works comes down to clean switching action and reliable working even in complex systems.
What is a DPDT switch?
A DPDT switch has six terminals that handle two independent circuits, where each input terminal connects to two output lines. The Double Pole Double Throw design allows switching between four separate paths using dual poles. I often use this type for setups needing quick changeovers between different input sources through clearly marked terminals. You can also read Double Pole Single Throw Switch.
Working of Double Pole Double Throw switch
A double pole double throw switch has six terminals that help control two independent circuits at once. Each input is connected to two outputs, allowing you to switch between separate paths with a Double Throw action. I’ve used this setup to make or break circuits in custom appliances with great success.
Many DPDT switches use momentary or maintained contact versions, and they operate like a dual ON-ON or ON-OFF-ON SPDT setup. I prefer the ON-ON style for its simplicity, especially when working with derived systems that require quick response. The switch design allows mutually active circuits and precise position control.
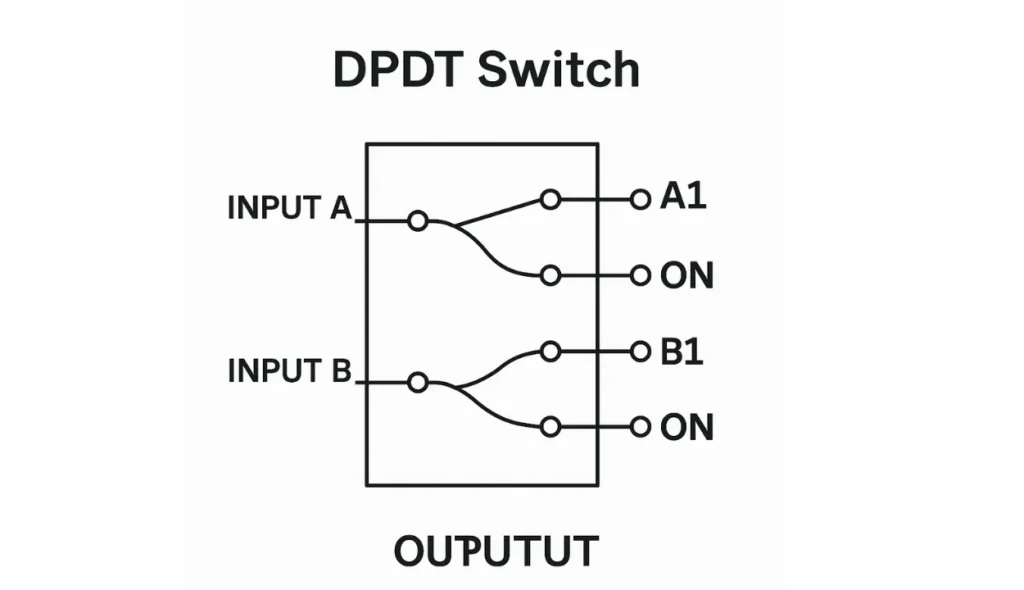
When the switch is ON, two circuits can be energized simultaneously, powering similar appliances at the same time. Through polarity reversal, it can even reverse motor directions, which I often do in automation. This design permits flexible switching between four circuits, ensuring the right conductors are always in position, whether up or down.
DC Motor Control using Double Pole Double Throw Switch
Controlling a DC motor with a double pole double throw switch is one of the easiest ways to reverse its direction. You just need to connect a battery and the motor across specific terminals like A, B, C, and D using proper wires and soldering methods. From my experience, keeping the circuit clean and following the correct diagram avoids confusion.
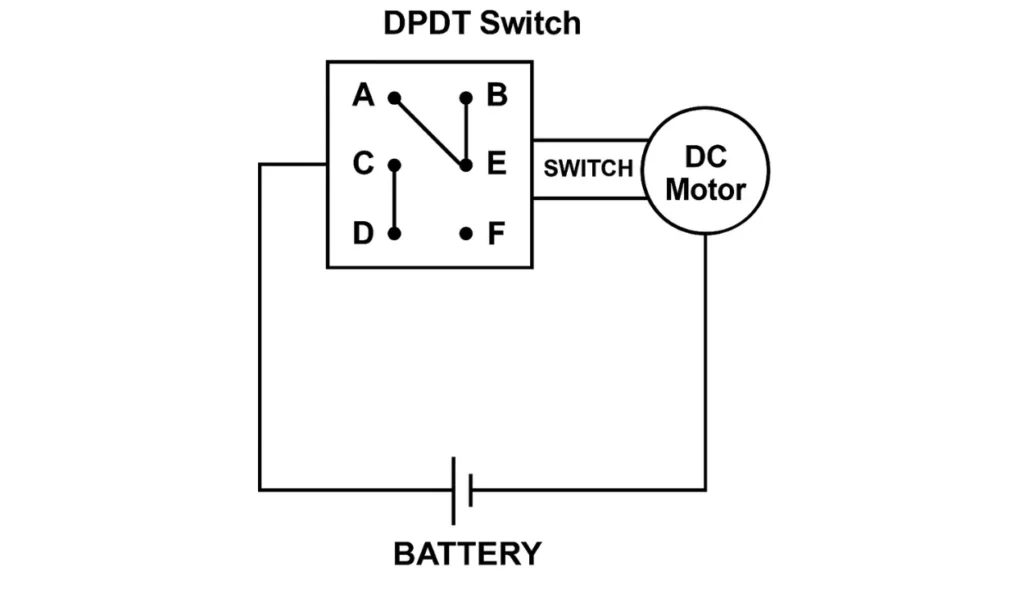
The switch has six terminals including E, F, and G which help manage the connection paths. By creating a connection between A & F and B & E, the motor gets properly connected and direction change is smooth. I always double-check each connection to ensure the circuit works before powering it up.
Working
To control a DC motor using a DPDT switch, I connect terminal-A to terminal-C and terminal-B to terminal-D for forward motion. When the switch is pressed in the forward direction, the motor rotates forward as the battery is allied in the correct connection. This setup is great when I need the motor to turn in one direction only.
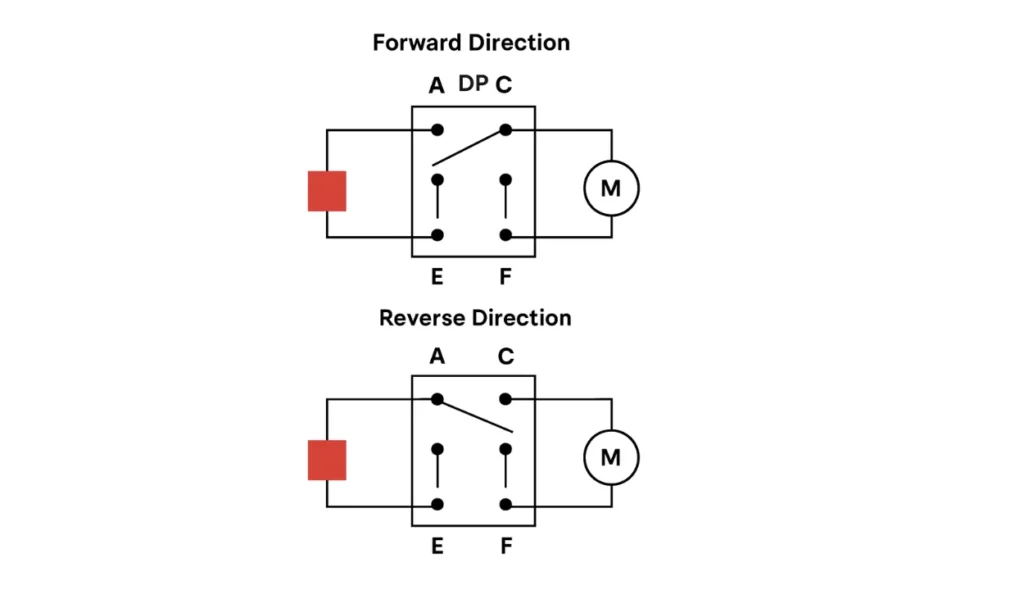
For reverse rotation, I just change the connection by linking terminal-C to terminal-E and terminal-D to terminal-F. When the switch is pressed in the reverse direction, the DC motor rotates in the opposite direction. It’s a simple way to switch between two directions using a few connected terminals.
DPDT Toggle Switch
The DPDT toggle switch comes in an On-Off-On configuration, rated up to 6A at 125VAC, and it can control two circuits or loads simultaneously. I’ve used this switch in boats, Jeeps, and RV’s, especially when waterproofing is essential—thanks to its sealed Marine-grade build. The diagram clearly shows how the switch manages different paths with ease.
It acts like two SPDT switches placed in one package, with each side having separate terminals that can be connected to one or two points. The toggle switch has a bat on the face and includes a dotted line showing the connection inside. I find this design simple yet powerful for handling ordinary and similar switch operations.

Advantages & Disadvantages of Double Pole Double Throw switch
Advantages
The DPDT switch can handle high voltages and current, making it ideal for powerful tasks.
It can drive motors, pumps, and control relays with ease.
It manages two independent signals at the same time without interference.
I’ve used this switch in multiple applications—it’s incredibly versatile.
The switching mechanism allows control over an appliance with just one flick.
It includes Failover capabilities, which keep operations running even during a fault.
The device is not expensive, yet it offers great features.
It’s also Less weight, so easy to fit into compact setups.
Disadvantages
When compared to bridges, it’s more expensive in network environments.
Network connectivity issues can’t be traced easily using this switch.
Handling broadcast traffic becomes difficult on this kind of switch.
Application of Double Pole Double Throw switch
A DPDT switch is commonly used in open and closed wiring systems to toggle between two different circuits.
I often use this switch for switching mains electricity, as it can separate both the neutral and live connections safely.
In robotics, this switch is ideal to control a robot, thanks to its reliable switching abilities.
It’s also great for reversing electric motors, where the switch is connected to achieve reverse polarity in a controlled way.
You can use a DPDT switch to operate two independent signals that work in tandem, which I’ve found handy in automation projects.
When switching is frequently used, this switch delivers consistent performance without fail.
Difference between Double Pole and Double Throw Switches
To recap, the primary difference is that double pole switches are great at controlling two circuits simultaneously, while double throw switches focus on switching between separate circuits.
When choosing the right switch, I always consider the specific electrical requirements and functionality needed for the system.
In marine setups like a boat, these switches are essential to handle the electrical load across the setup with the correct functionality.
From experience, understanding the factors involved—like your desired outcome and how many circuits are involved—is key for the perfect match.
Conclusion
The Double Pole Double Throw (DPDT) switch stands out as a highly versatile component, offering precise control over multiple circuits with a single compact device. Whether you’re reversing a DC motor, building a robotic system, or managing marine electrical setups, the DPDT switch proves to be both reliable and adaptable across diverse applications.
With configurations like ON-ON or ON-OFF-ON, and the ability to handle high voltages, currents, and dual circuits, it’s a practical solution for engineers and hobbyists alike. From my hands-on experience, its simple installation, durable build, and flexibility make it a go-to choice when smart, controlled switching is required in any project.


