Introduction
In the early days, a fuse was the most common choice for protection against overcurrent, but it had a major drawback. The metal wire inside melts when excess current flows, stopping the circuit but requiring a replacement. Over time, this was replaced by a more efficient and small electronic device—MCB (Miniature Circuit Breaker). Unlike a fuse, an MCB does not require replacement after interrupting the power; it can be switched back on. This article explores the details of how MCBs work and why they are a smarter choice for electrical circuits in modern appliances and devices, ensuring safety and preventing damage from fluctuations, overloads, and short circuits.
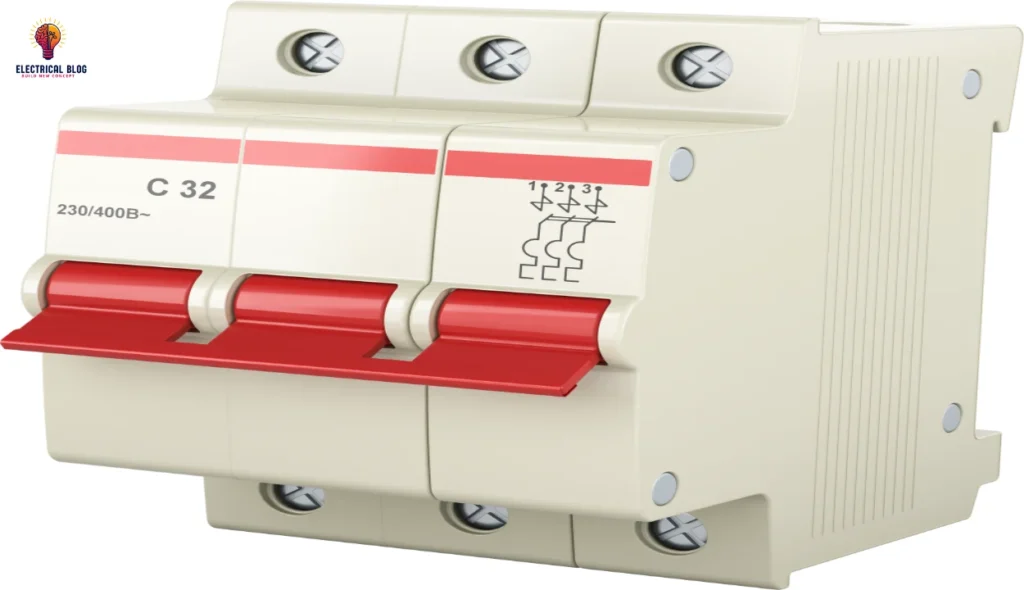
What is a miniature circuit breaker?
In every household, electrical appliances like washing machines, ovens, and fridges rely on a steady current flow. But when an excessive surge or short circuit occurs, it can lead to serious accidents, causing fires or burnt components. A fuse was once the alternative, but it had to be rewired or replaced after every trip. Today, the Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB) is the better solution, ensuring safety without frequent replacement.
An MCB is an automatic switch that opens when it detects a fault in the circuit, preventing damage. It is built with an electromechanical mechanism, including a bi-metal strip and solenoid, to react quickly to overload and protect the system. Unlike traditional breakers, it can be easily reset after it shuts off due to an issue. This proper function ensures a continuous supply without additional costs or extra handling.
Once installed, an MCB works efficiently to maintain safe operations in all types of breakers and electrical systems. It automatically recloses after resolving the issue, restoring power. Whether in homes or industries, its principle remains the same—detecting irregular flows and cutting power to prevent failures. With low maintenance demands, it offers long-term reliability and effective protection for essential electrical accessories.
Different Types of Miniature Circuit Breakers
MCB selection depends on the type and application of electrical devices. Each MCB has a unique trip curve designed to handle different loads and prevent short-circuit faults. The choice of MCB ensures proper protection for residential, commercial, and industrial systems.
A Type MCB is highly sensitive and trips off when the actual current exceeds 2-3 times its rating. It is widely used in the semiconductor and manufacturing industries where precision is required. This MCB ensures safety by reacting instantly to electrical surges.
B Type MCB trips when the flow exceeds 3-5 times the standard limit and is commonly used in cable protection. It is ideal for domestic environments where appliances need a controlled power supply. This type is best suited for homes and small offices.
C Type MCB handles higher loads and trips at 5-10 times the rating, making it suitable for IT systems like servers, computers, and printers. It is also used in fluorescent lighting and transformers to manage power fluctuations.
D Type MCB can withstand surges up to 10-20 times the rating and offers high resistance. It is best for motors, compressors, and heavy-duty industrial machinery. This makes it ideal for setups requiring stable power control.
K Type and Z Type MCBs are designed for specific uses, such as winding machines and X-ray equipment. These breakers trip quickly under certain conditions, offering strong protection for specialized electrical systems.
Miniature Circuit Breaker Types
Different types of Miniature Circuit Breakers (MCBs) are designed to handle various electrical conditions. The voltage, current, and characteristics of each breaker determine its use. Selecting the right MCB ensures proper protection and prevents electrical faults.
Thermal MCBs rely on temperature changes to detect overloads. A bimetallic strip bends when the temperature rises, causing the trip mechanism to activate. This kind is frequently utilized in both residential and commercial environments.
Magnetic MCBs operate based on the force generated by electrical flow. When the current exceeds the allowed limit, a solenoid pulls the internal mechanism, triggering the trip. This type is ideal for short-circuit protection.
Hybrid MCBs combine both thermal and magnetic properties for better performance. These breakers respond to overloads and short circuits more accurately. They are used in systems where both issues must be addressed efficiently.
Residual Current Circuit Breakers (RCCB) protect against electric shocks and earth leakage. They monitor the neutral and current flowing through a circuit. If an imbalance is detected, they instantly trip, preventing severe accidents.
Differential MCBs are designed for DC circuits and offer advanced protection. They detect faults by analyzing the difference in electrical currents and react faster. These are essential for modern electrical safety.
Isolation MCBs serve as a switch to isolate electrical circuits. Unlike other breakers, they do not have a trip function. They are primarily used for testing and maintenance purposes in electrical systems.
Each MCB is selected based on different factors, ensuring proper safety. Choosing the right type improves reliability and prevents fire hazards. Understanding these variations helps in selecting the best MCB for any application.
Working Principle of MCB
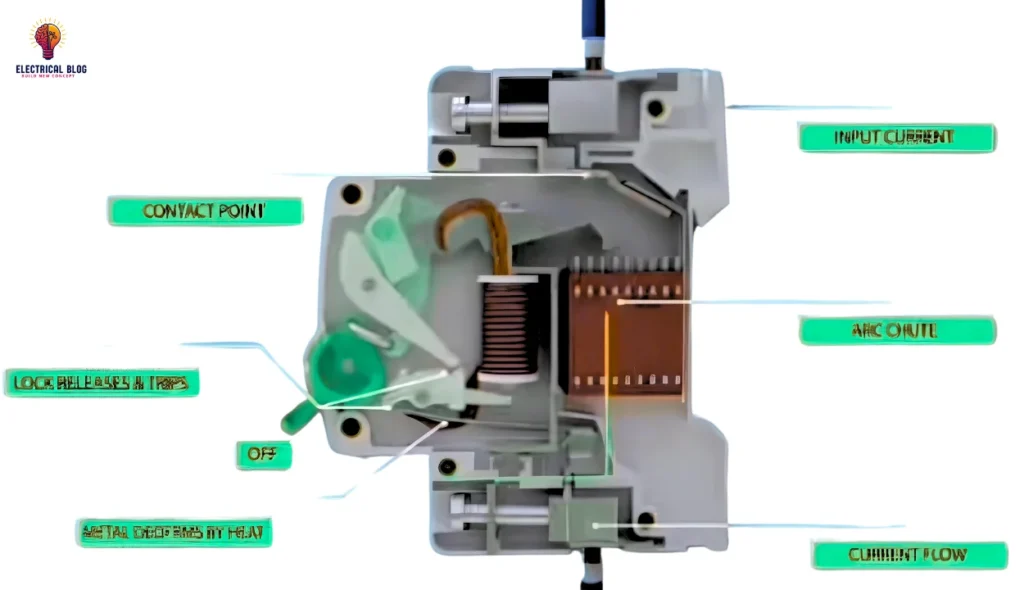
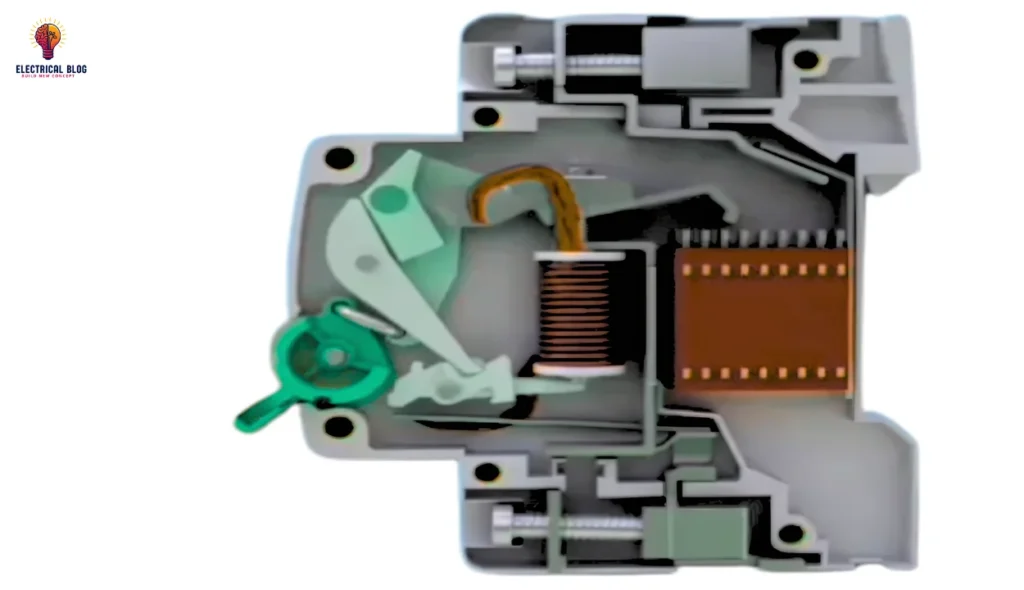
A Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB) is designed to safeguard electrical devices by preventing overload and overcurrent conditions. When the incoming flow of current exceeds the safe limit, the bi-metallic strip inside the unit gets heated and deflects. This movement releases the latch, causing the breaker to turn off and stop the hazards of overheating. The system remains maintenance-free and can be manually restarted after the issue is resolved.
During a short circuit, the electromagnet inside the MCB plays a key role in protection. The sudden rise in current generates a strong magnetic force that moves the plunger and hits the lever. This action triggers the automatic release of the latch, leading to the opening of the contacts and breaking the circuit instantly. This quick response ensures that electrical faults do not cause severe damage.
Inside the MCB, the Arc Chutes and Holder help control the electrical arc generated during the trip process. The dynamic movement of the components efficiently directs the arc into the Chutes, reducing stress on the fixed and outgoing terminals. This structured mechanism allows the breaker to function effectively and enhances its lifespan.
MCBs are installed on a DIN rail for easy operation and replacement. If damaged, they can be replaced without complex wiring. These operable breakers provide a reliable way to protect circuits, making them a crucial component in modern electrical systems.
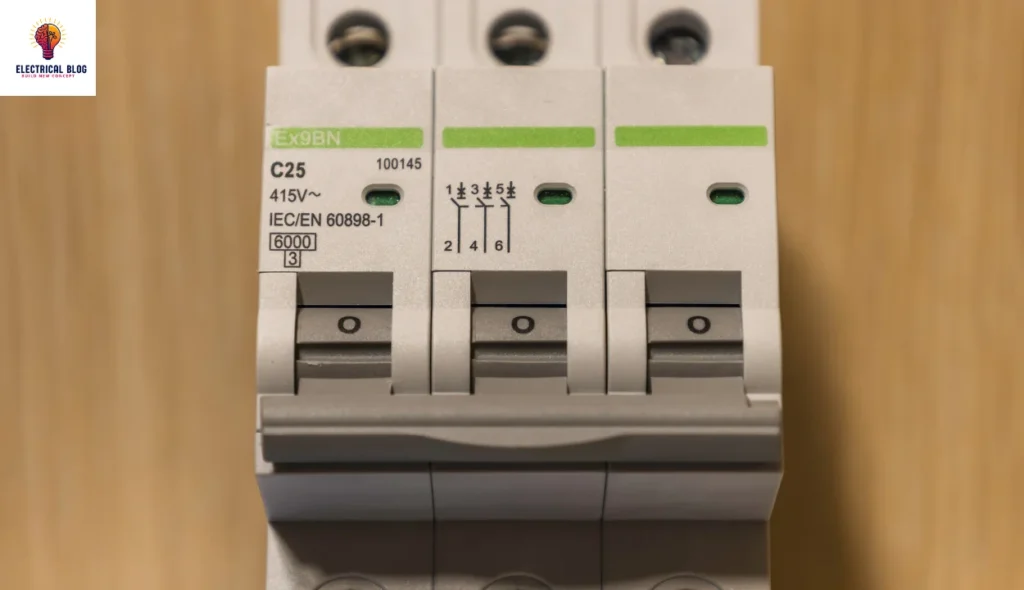

Uses of MCB
MCB is a key component in both industrial and domestic setups, ensuring safety in electrical systems. It is used to protect various appliances, including lights, heaters, and fans, by preventing overload and short circuits. By constantly checking the connection, it maintains the efficient functioning of machines and other devices. This makes MCBs essential for different purposes in electric systems, offering reliable use.
Conclusion
MCBs play a crucial role in ensuring the safety and efficient functioning of electrical systems in both domestic and industrial settings. By constantly checking the connections and preventing overload, they protect essential appliances like lights, heaters, fans, and machines. Their reliable use makes them a key component in modern electric systems, providing long-term security and stability.
FAQs
What is the advantage of a miniature circuit breaker?
A Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB) provides better safety and protection compared to traditional fuses. It can automatically trip during an overload or short circuit and can be reset without needing a replacement. MCBs are efficient, reliable, and maintenance-free, making them ideal for both domestic and industrial applications.
What do you mean by a miniature circuit breaker?
A Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB) is an electrical safety device designed to protect circuits from overcurrent, short circuits, and overload conditions. It automatically disconnects the circuit when abnormal current flows, preventing damage to appliances and reducing the risk of fire or electrical faults.
What is the difference between an MCB and a fuse?
An MCB and a fuse both serve as protective devices, but an MCB is more advanced. A fuse melts when excessive current flows, requiring a replacement after every trip. In contrast, an MCB automatically trips and can be reset manually, making it more reliable and cost-effective over time.
What is the standard current rating for MCBs?
MCBs come in different current ratings, typically ranging from 0.5A to 125A, depending on their application. For domestic use, the standard ratings are 6A, 10A, 16A, 20A, 32A, and 40A, while industrial settings may require higher ratings based on power demand.
What is the difference between a Type B and a Type C MCB?
A Type B MCB trips when the current exceeds 3-5 times the rated limit, making it suitable for residential applications such as lights and heaters. A Type C MCB trips at 5-10 times the rated limit and is ideal for commercial and industrial settings, including transformers, motors, and fluorescent lighting.