Introduction
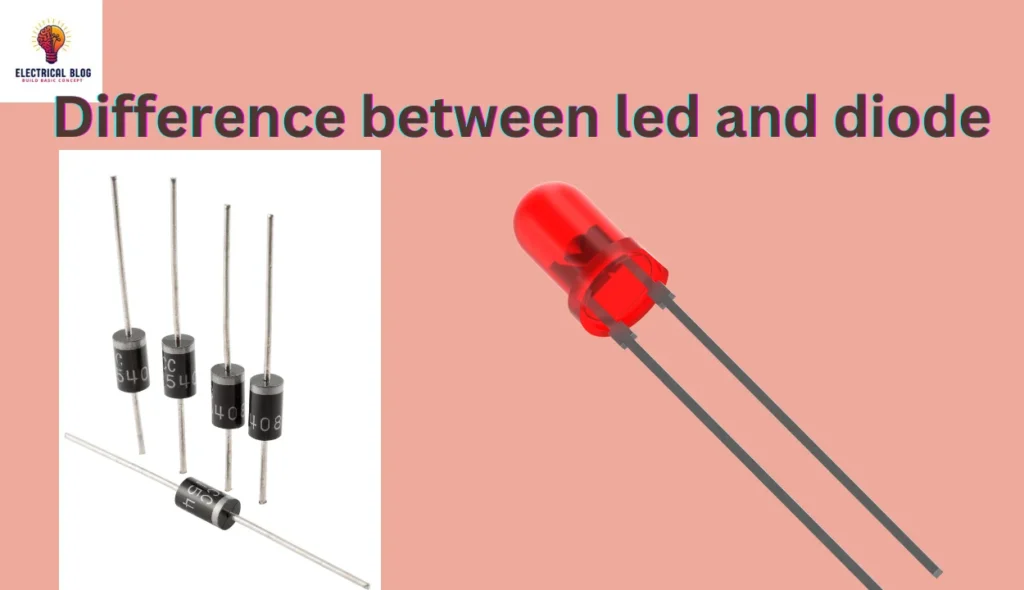
LED and diode are both essential electronic components with a significant role in electric circuits. The key difference lies in their function; while a diode mainly allows current to flow in one direction, an LED also emits light when current passes through it.
The properties of LEDs make them efficient in converting energy into light, while a standard diode is better for pure conduction without affecting the circuit with heat. Materials like germanium, arsenide, and phosphide influence their performance, and a comparison chart often highlights how electrons and holes move in their valence bands under current flow.
What is an LED?
An LED is a special type of diode that emits light using a process called electroluminescence. This phenomenon occurs when electrons and charge carriers recombine in a semiconductor material under forward-bias conditions.
In an LED, the N-region holds electrons (the majority carriers), while the P-region contains holes. When forward bias is applied, these carriers recombine, releasing energy in the form of photons, producing light with low heat output.
Materials like GaAs, GaP, and silicon are common in LED manufacturing, while germanium is rarely used. Compared to standard diodes, LEDs are smaller, require less power, and are available in various color options for different applications.
However, LEDs can be damaged if exposed to overvoltage or overcurrent. They are ideal for low DC power circuits but must be carefully managed to avoid no lights or burnout issues.
From personal experience, using LEDs effectively in small-area lighting projects saves energy and ensures durability. Their compact size and efficient conduction make them perfect for designs requiring controlled power consumption.
What is a diode?
A diode is a two-terminal semiconductor device designed to control current flow. It has n-type and p-type materials that are connected to form a junction. This structure allows current to move in only one direction.
The anode is positive, and the cathode is negative, enabling it to act as a rectifier. When voltage is applied in the forward bias, the diode conducts easily with a small voltage drop, while reverse bias causes it to block current. This behavior makes diodes reliable conductors in electronic circuits.
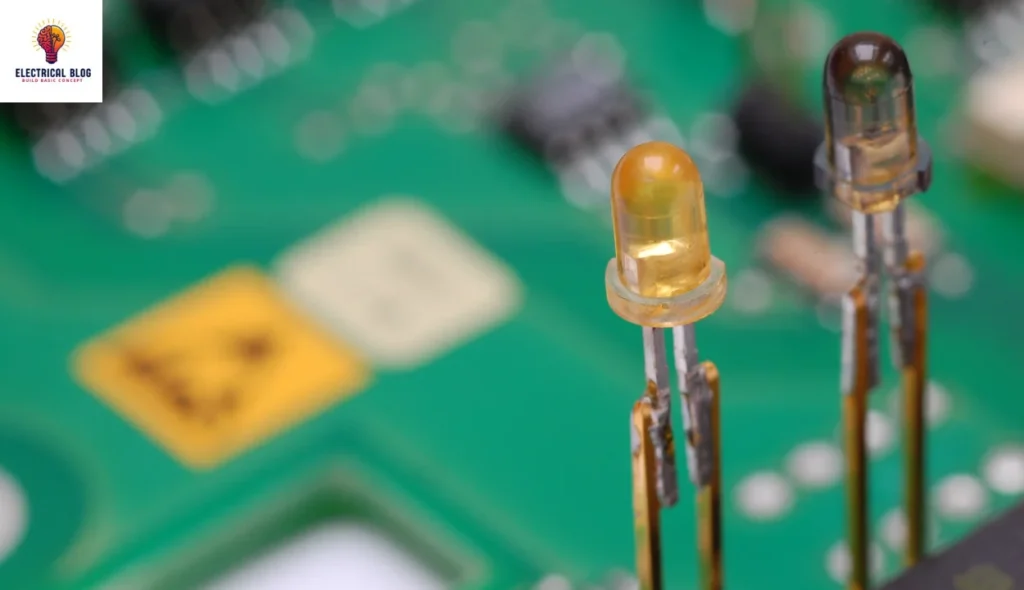
Key differences between the LED and the diode
An LED is a semiconductor device that emits energy as light, while a diode mainly rectifies alternating current by allowing flow in one direction.
LEDs are made from gallium, arsenide, or phosphide, while diodes commonly use silicon or germanium as their materials.
LEDs require a higher on-state voltage of around 1.2 V to 2.0 V, while diodes operate at a low voltage of 0.7 V for silicon and 0.3 V for germanium.
LEDs release heat as energy, while a diode primarily prevents excessive heat during conduction.
LEDs are used in headlamps, signals, medical devices, camera flashes, and automotive lights, whereas diodes are essential in clipping, clamping, circuit protection, rectifiers, and multipliers.
LEDs are designed to glow, while diodes have a low visual output and focus only on transferring electrical signals.
LEDs do not work in reverse bias, while diodes can handle reverse breakdown conditions without damage.
LED vs Diode
| Feature | LED | Diode |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Converts electric energy into light | Used for rectification and signal control |
| Material | Made from GaAs, GaP, Gallium, Arsenide, or Phosphide | Uses Germanium or Silicon |
| Voltage Requirement | Requires 1.2v to 2.0v to operate | Operates at 0.7v for Silicon and 0.3v for Germanium |
| Energy Efficiency | Efficiently transfers energy with minimal heat loss | Generates heat during operation |
| Application | Common in indicators, seven-segment displays, and light sources | Widely used in multipliers, clamping, and rectification circuits |
| Current Type | Operates on DC power only | Works with both AC and DC power |
| Direction Control | Allows current flow in only one direction with visible light output | Controls current flow in one direction without visible light |
Conclusion
Both LEDs and diodes serve important roles in electronics but have different purposes. While LEDs emit light and are designed for visual output, diodes focus on controlling energy flow. The choice depends on circuit needs and properties like heat tolerance and efficiency.
LEDs use gallium, arsenide, or phosphide to produce light, while diodes are often made from silicon or germanium for better conductivity. Each material has unique advantages, ensuring devices operate efficiently with minimal heat loss.
Read more: SVC Electrical