Buchholz Relay: A Transformer Safety Solution
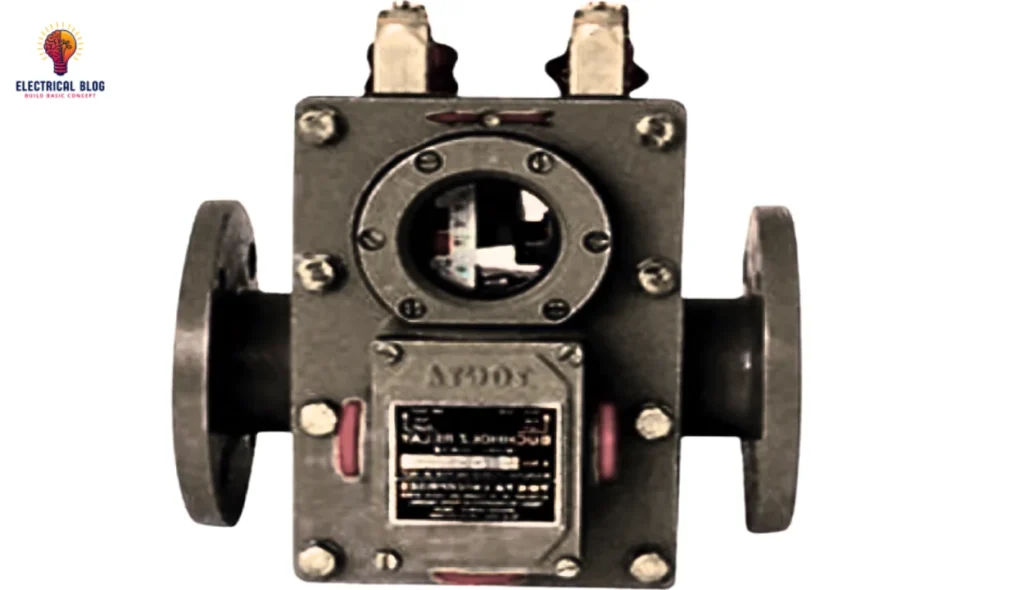
What is a Buchholz relay? A Buchholz relay is a protective safety device used in oil-filled transformers and reactors to detect faults early. It operates by sensing gas formation, which can occur due to dielectric failure inside the equipment. Positioned in the main oil circuit, it connects the transformer to an external reservoir, known as […]