Introduction
Busbars are essential components in electrical systems, playing a critical role in the distribution of power. They act as centralized hubs that streamline electrical connections, offering both cost and efficiency benefits. By replacing multiple individual conductors, busbars simplify wiring and reduce material costs. However, while they bring numerous advantages, including enhanced protection and flexibility, there are also certain disadvantages, such as higher installation costs, space requirements, and potential maintenance challenges. Understanding both the pros and cons of busbars, especially when comparing copper and aluminium options, is essential for making informed decisions in power system design.
What is an electrical busbar?
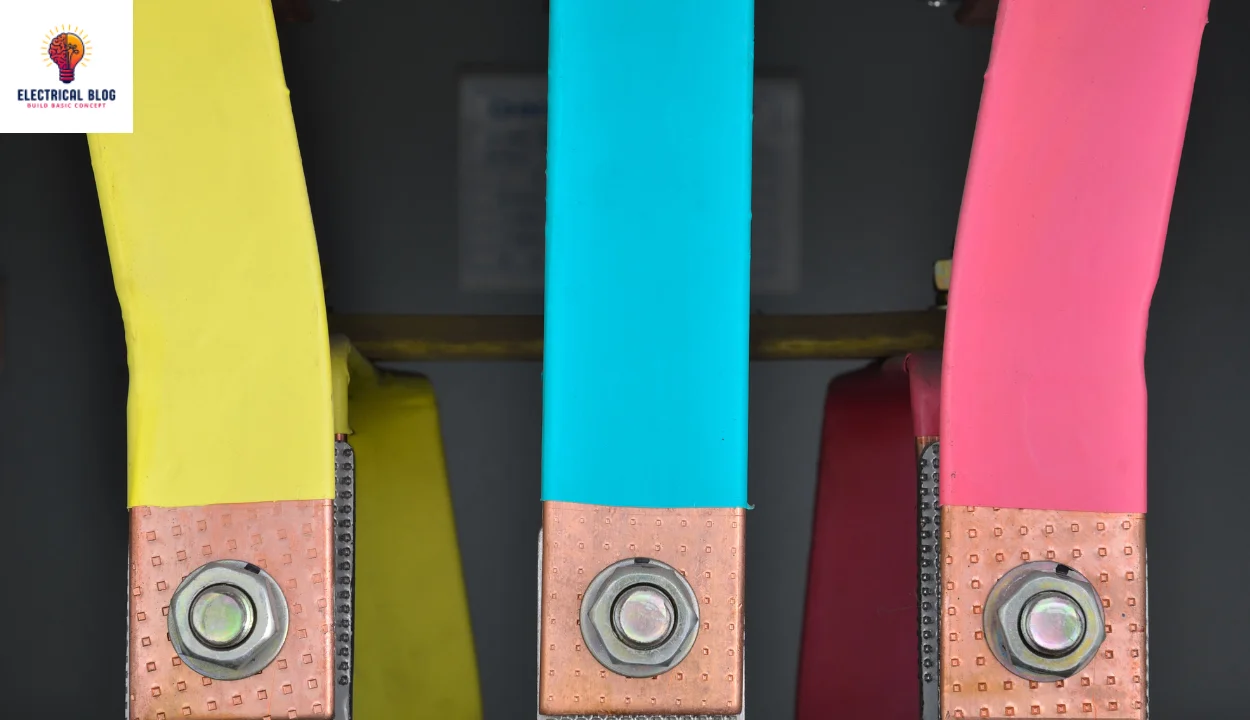
An electrical busbar is a central component that operates as a metallic conductor, efficiently managing currents within systems. Acting as a link, it allows incoming and outgoing electricity to converge, ensuring seamless power distribution. These connectors can be solid, hollow, or flexible, depending on the applications and demands of the electrical setup. Their configuration is tailored to different voltage levels, such as low, medium, and high, to optimize performance.
The realm of substations heavily depends on busbars, making them an indispensable part of power networks. They are found in various types, supporting everything from residential wiring to industrial grids. Some handle approximately 11kV, while others go beyond 765kV, proving their versatility across a range of uses. With the right designs, they can efficiently carry electricity while balancing advantages and disadvantages based on the environment.
From my experience, the true strength of a busbar lies in its ability to connect multiple electrical elements with precision. In high-demand power setups, its capacity determines stability, ensuring efficient energy transfer at critical crossroads. Whether for small-scale or large-scale systems, its role is undeniable, making it a key point in modern electrical infrastructure.
The Importance of Busbars in Power Distribution
A busbar plays a vital role in power distribution by making energy flow more straightforward and efficient. It helps supplant multiple individual conductors, leading to significant cost reductions. With a unified nodal point, it ensures smooth incoming and outgoing connections, optimizing performance. The incorporation of protective measures further enhances safety, making it an affordable and practical choice.
In modern systems, they are integrated with components like isolators and breakers to handle faults effectively. When a faulty section is detected, the breaker is activated, isolating the issue from the circuit. This configuration prevents disruptions and ensures a stable connection. With its adaptable design, a busbar simplifies maintenance, proving its reliability in various power setups.
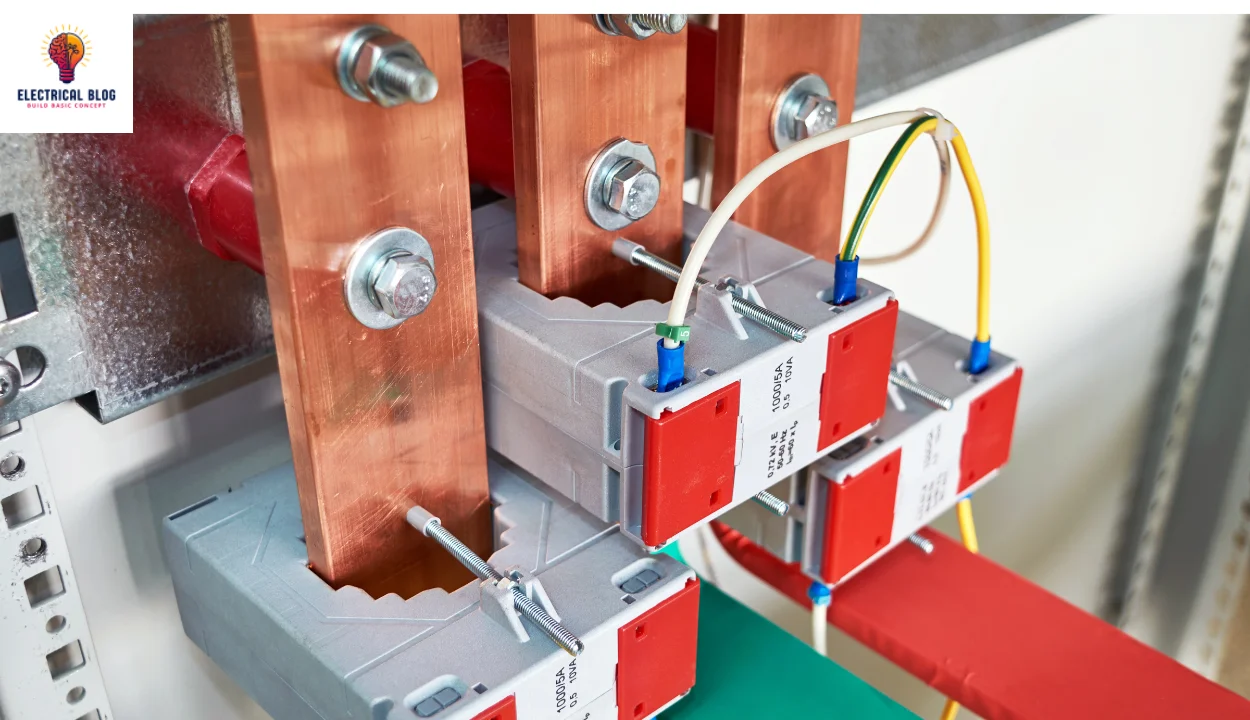
Different Types of Busbars
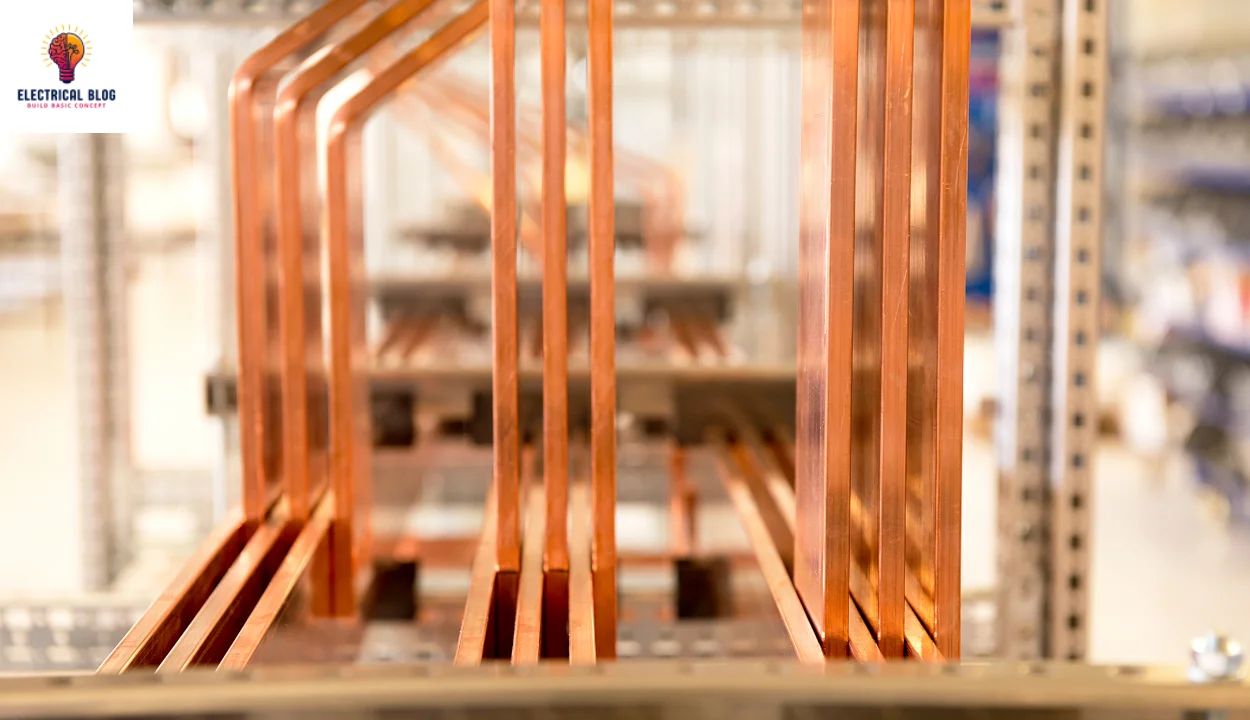
They come in diverse shapes, including rectangular, circular, and cross-sectional, each designed for specific needs. Their construction primarily relies on copper or aluminium, and the right material depends on various considerations like conductivity and durability. To select the best option, one must explore an array of factors, as the choice hinges on the application’s power demands.
Copper Busbars
Copper is the benchmark for conductivity, offering unparalleled performance in electrical scenarios requiring high efficiency. Its historical use proves its reliability, with strong tensile strength, excellent thermal expansion, and superior corrosion resistance. Though heavier and more expensive than aluminium, its efficacy in conduction makes it ideal for applications demanding durability and resistance to organic chemicals.
Aluminium Busbars
Aluminium busbars are preferred for their lighter weight, making transportation and installation easier while offering significant savings. Though their conductivity hovers around 62% of copper, they are more affordable and efficient for large-scale projects. Their mechanical strength varies based on alloying agents, allowing customization for different needs. However, aluminium necessitates larger surface areas for an equivalent power flow, making them bulkier than copper alternatives. Despite this, their potency and steel-like durability in some compositions distinguish them in various applications. This balance of cost, durability, and strength makes aluminium busbars a practical choice in modern electrical systems.

Comparative Analysis of Copper Busbars and Aluminium Busbars
Copper offers better electrical performance with lower resistance, reduced voltage drop, and higher ampacity, making it ideal for high-power applications. On the other hand, aluminium prevails in weight-based efficiency, making it a cost-effective alternative in large-scale projects.
Sustainability is a key factor, as aluminium recycling has a lower energy footprint, with around 75% of produced aluminium still in circulation. Both metals are recyclable, but copper requires more energy for processing, affecting its environmental impact.
Material costs are influenced by market dynamics and socioeconomic factors, where copper outweighs aluminium in price. However, price fluctuations can occur, making it crucial to consider long-term comparisons based on project application and budget.
Connector considerations are essential when opting for aluminium, as it requires compatible ratings for safety. While copper connectors can often work with aluminium, the reverse isn’t always true, adding an extra layer of attention to the decision-making process.
Advantages of Electrical Busbars
Busbars improve power distribution by replacing multiple conductors, reducing costs and material usage, while making installations more efficient.
Their flexibility allows for different configurations, adjusted to meet varying requirements, making them suitable for diverse applications.
Ensuring system continuity, certain arrangements, like main and transfer setups, help maintain power even during maintenance or faults.
They help safeguard systems by facilitating the integration of protection devices, preventing overloads, and minimizing risks.
Busbars simplify maintenance procedures, offering easy access to components, reducing downtime, and making fault isolation faster.
Their environmental benefit lies in sustainability, as both copper and aluminium options are recyclable, contributing to resource conservation.
Localized faults are handled efficiently, as ring setups can isolate faulty segments, reducing the impact on the entire system.
By streamlining the electrical integration, busbars create a central hub, ensuring reliable performance with minimal disruption.
Disadvantages of Electrical Busbars
Busbar installation can involve a higher initial investment compared to traditional wiring systems, impacting overall project costs.
They can be complex, requiring skilled design and installation to avoid operational issues.
Space requirements for busbars can be more than wiring, especially in certain arrangements, limiting their use in tight spaces.
Copper busbars are heavier, which might necessitate additional structural support during installation.
Material prices, like copper and aluminium can fluctuate due to market conditions, affecting the project budget.
Choosing the wrong connector compatibility, like using aluminium connectors for copper busbars, can lead to operational problems.
Overload risks may arise, particularly in ring main arrangements if circuit breakers are opened, creating potential hazards.
The complexity of busbar systems may result in higher maintenance costs, requiring more resources to manage than simpler systems.
Conclusion
While they offer many advantages, such as simplified distribution, cost savings, and enhanced protection, they also come with certain disadvantages. Higher installation costs, space requirements, and complexity in design and maintenance are factors to consider. Additionally, material price fluctuations and connector compatibility issues can influence project budgets and performance. Copper and aluminium each bring their own set of benefits and challenges, so choosing the right busbar for your specific needs depends on balancing these factors for optimal efficiency and cost-effectiveness.




