Introduction to Alternators vs Generators
When it comes to producing electricity, both an alternator and a generator play key roles, yet they operate differently. An alternator generates electrical energy by allowing its magnetic field to rotate around a stationary armature, while a generator works oppositely, with the armature rotating inside a stationary magnetic field. Despite their shared purpose of converting mechanical energy into power, these mechanical devices exhibit clear differences in functionality.
I once tested both systems in a workshop, and understanding how the armature behaves made the contrast clearer. While the alternator’s rotating system felt smoother and more efficient, the generator seemed more robust yet slightly outdated. Knowing these differences helps in choosing the right system for various electrical needs.
Electricity Generation
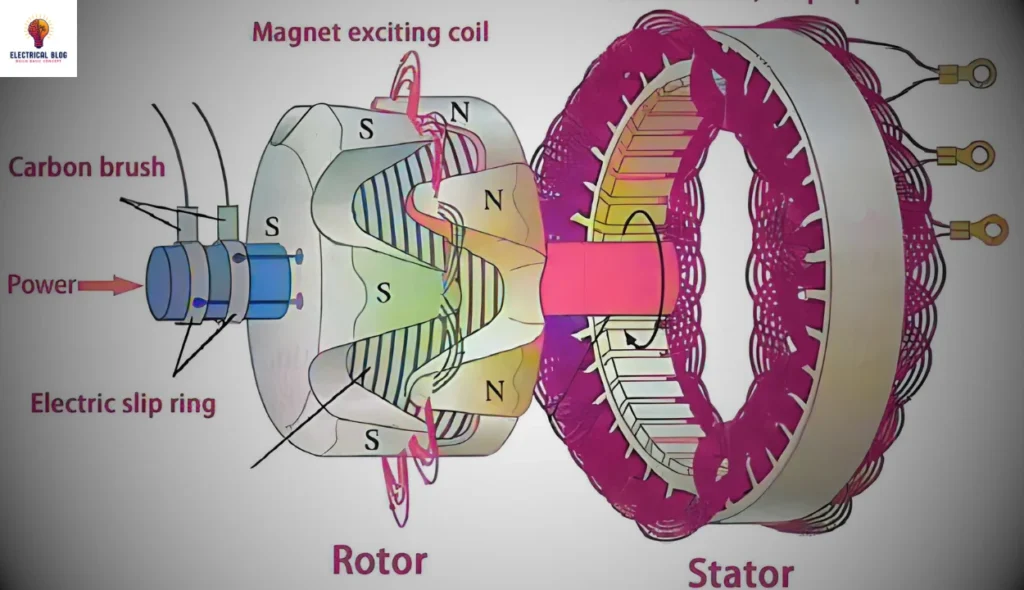
Electricity is generated through Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction, where a magnetic field acts on a conductor to create an electric current. This principle applies to both an alternator and a generator, where either the rotor rotates inside a stationary conductor or the magnetic field spins around a stationary coil. As the magnetic effect varies, it induces an EMF, causing current to flow.
I’ve seen this process firsthand in a workshop where a rectangular coil inside the housing had to keep changing position for efficient energy production. The machine parts, like the stator and rotor, must work in harmony, ensuring the magnetic field properly intersects the coil. This constant movement induces power efficiently, proving the clever design behind these devices.
What is an alternator?
An alternator is a mechanical device designed to convert mechanical energy into AC electrical energy. It features a rotor that keeps revolving to create a magnetic field acting on the stationary armature conductors. This movement causes the magnetic field lines to keep changing, which induces an electric current. The generated power is then supplied to the output load based on what is required.
The alternator is highly efficient because it only produces energy when the load demands it, helping to conserve power. Unlike older generator models, it prevents overcharging in batteries by automatically stopping the power flow when not needed. The rotation can be driven by combustion engines, steam turbines, or gas turbines, known as the prime mover. With this design, the alternator prevents energy waste while ensuring reliable performance.
For durability, the alternator uses brushes that face minimal wear due to the stationary armature setup. This improves mechanical life and reduces maintenance needs. The electromagnet in the housing can use a DC supply, or a permanent magnet may replace it. Whether powering a vehicle or charging a partially drained battery, the alternator effectively manages energy flow with precise polarity control in the north and south directions. You can also read Permanent Magnet Synchronous Generator.

What is a generator?
A generator is a mechanical device that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy, producing both AC and DC. Inside the outer housing, the stationary electromagnet or permanent magnet creates magnetic field lines that interact with the rotating armature. As the armature rotates around its axis, the magnetic field lines keep varying, which induces an electric current. This movement results in a steady output voltage during operation.
The generator uses either a slip ring for alternating current or a commutator for direct current, which keeps the output current flowing in one direction. The commutator includes breaks that reverse the current’s path after each half rotation. This design ensures constant energy flow, making the generator ideal for backup power in homes, offices, and construction sites. It is also effective for charging a completely drained battery.
From my experience, generators provide power constantly, even when not needed, lowering efficiency. Unlike an alternator, they lack an automatic stop feature, which may lead to energy waste. However, their ability to transfer power steadily makes them suitable for critical power supply needs where reliable output is essential. You can also read Synchronous Generators.

Difference between Alternator and Generator
| Feature | Alternator | Generator |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | An Alternator is a device that produces AC electrical energy by converting mechanical energy. | A Generator is a mechanical device that produces both AC electrical energy and DC electrical energy. |
| Output Current | An Alternator always induces alternating current. | A Generator can generate alternating current or direct current. |
| Energy Efficiency | Alternators are highly efficient and conserves energy by using only the required amount. | Generators are less efficient as they use all the energy that is produced. |
| Output Power | Alternators deliver a higher output. | Generators provide a lower output. |
| Voltage Generation | Alternators produce voltage only when required. | Generators produce voltage at all times. |
| Energy Conservation | Alternators save more energy by supplying power only when needed. | Generators conserve less energy since they constantly produce power. |
| Armature Movement | The armature in an Alternator is stationary. | The armature in a Generator is rotating. |
| Magnetic Field | The magnetic field in an Alternator is rotating inside the stator. | In a Generator, the magnetic field is fixed while the rotating armature spins inside it. |
| Input Supply | An Alternator takes its Input Supply from the stator. | A Generator takes its Input Supply from the rotor. |
| RPM Range | Alternators operate at a wide range of RPM. | Generators run at a lower RPM range. |
| Brush Efficiency | The brushes in an Alternator last longer because they experience less wear. | The brushes in a Generator last lesser as they endure more friction. |
| Polarization | Alternators do not require polarization after installation. | Generators need polarization after installation. |
| Size | Alternators are smaller and require less space to fit. | Generators are larger and need larger space for installation. |
| Charging a Dead Battery | Alternators will never charge a dead battery. | Generators can be used for charging a dead battery. |
| Uses | Alternators are widely used in the automobile industry as part of the charging system. | Generators are ideal for producing large-scale electricity and are often used as backup power in homes, offices, and construction sites. |
Conclusion
In the comparison between alternators and generators, both play crucial roles in converting mechanical energy into electrical energy. Alternators are great for saving energy and are efficient. They work well in vehicle charging systems. Generators, on the other hand, are more versatile. They can produce both AC and DC currents. This makes them ideal for backup power in homes, offices, and construction sites.
Understanding their differences in output, RPM range, and energy usage can help in selecting the right device for specific needs. Ultimately, choosing between them depends on the required voltage, application, and available space.