Introduction
A universal motor is a special type of electric machine that runs on both AC and DC supplies. This unique ability makes it a preferred choice for various applications where flexibility is required. The principle behind its working is the interaction of electrical and magnetic fields, which allows it to achieve high speed and efficient energy conversion.
For students eager to learn, this article explores what makes a universal motor different, its concepts, and how it is divided into various types. The electromechanical structure of this motor helps in transforming electrical energy into mechanical energy, making it a vital component in power tools and household devices. A detailed diagram further illustrates its design, enhancing understanding.
What is a universal motor?
A universal motor is a unique type of motor designed to operate on both AC and DC power sources. It has a series-wound design where the armature and field windings are connected in series, allowing it to generate high torque. These motors are built into the device they are meant to drive, making them ideal for compact applications.
What makes a universal motor unique is its ability to operate at very high speeds, often reaching 3,500 RPM. It achieves a higher speed on DC supply than on AC supply due to the reactance voltage drop, which is only present in AC circuits. This feature allows it to function efficiently with different power supplies while maintaining strong performance.
Universal motor diagram
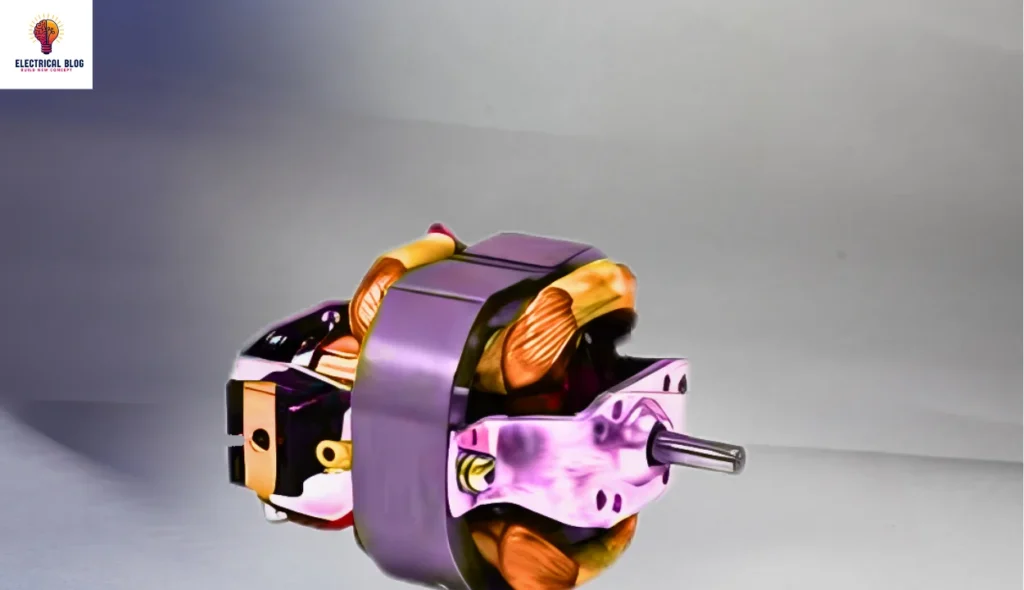
Structure of a Universal Motor
A universal motor has a stator with poles mounted on it, and field coils wound around them. The armature is laminated to reduce eddy currents that are produced while operating on AC power. These laminations improve efficiency and prevent overheating in high-speed applications.
The rotary part of the motor contains slots, which can be straight or skewed, where the commutator and brushes rest. The commutation on AC is poorer than on DC due to the current induced in the coils, requiring high-resistance brushes. This helps maintain stable performance in both power modes. You can also read stepper motors.
Operation of Universal Motor
Behavior with a DC supply
When a universal motor is fed with a DC supply, it works as a series motor. The current flows through the winding and armature conductors, creating a strong electromagnetic field. As a result, the rotor experiences a mechanical force, which causes it to rotate continuously.
According to Fleming’s left-hand rule, when a current-carrying conductor is placed in a magnetic field, it moves in a specific direction. This principle helps in determining the movement of the rotor in a universal motor. The interaction of the field and conductor ensures smooth performance under DC supply conditions.
How It Works with AC Supply
When a universal motor is supplied with AC power, it generates unidirectional torque due to its connected series winding. As the current in the armature and field reverses, the magnetic direction also changes. This ensures that the force experienced by the conductors always remains the same.
The polarity of AC shifts continuously, but the motor still works like a DC series motor due to its principle of synchronized reversal. Regardless of the supply, the phase shift allows the torque produced to stay steady, keeping the motor running efficiently.
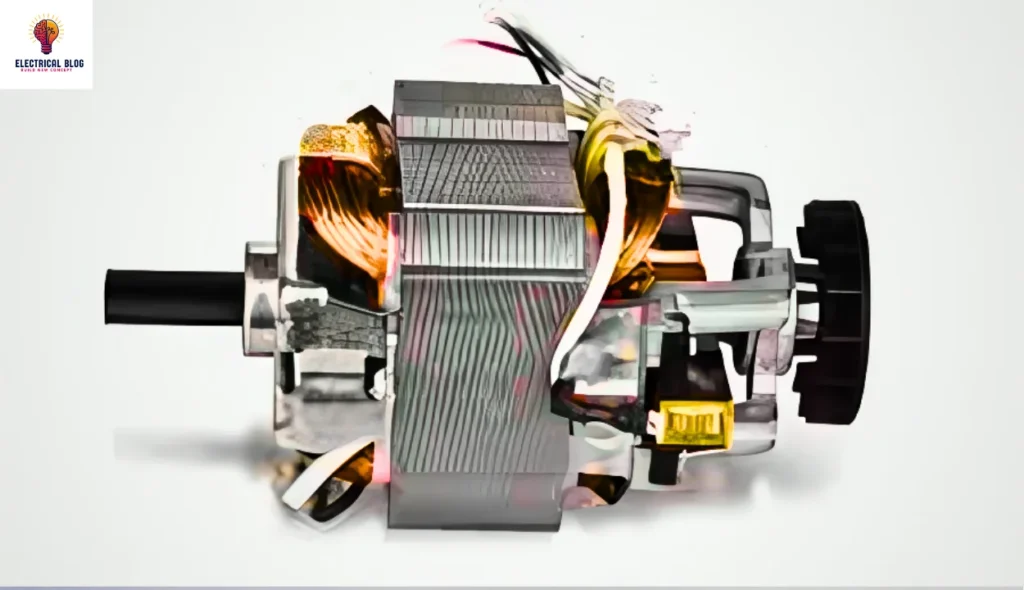
Types of Universal Motors
Non-compensated Motor
A non-compensated motor is built with two wide poles and a laminated core for better efficiency. The armature is wound in a specific form, with the winding leads attached to a switch. It features skewed or straight slots and high-resistance brushes to enable improved commutation.
Compensated Motor
A compensated motor involves a stator core with a connection to a split-phase system. It has scattered field windings and an additional winding to manage the alternating flow. This design decreases the voltage reaction, improving efficiency and performance.
Properties of Universal Motors
Universal motors can run at high speeds, making them ideal for tools and appliances that need quick operation.
They offer high starting torque, allowing them to handle heavy loads efficiently at the start.
Their compact size and lightweight design make it easy to fit into small devices.
Due to the commutator and brushes, they can be noisy during operation.
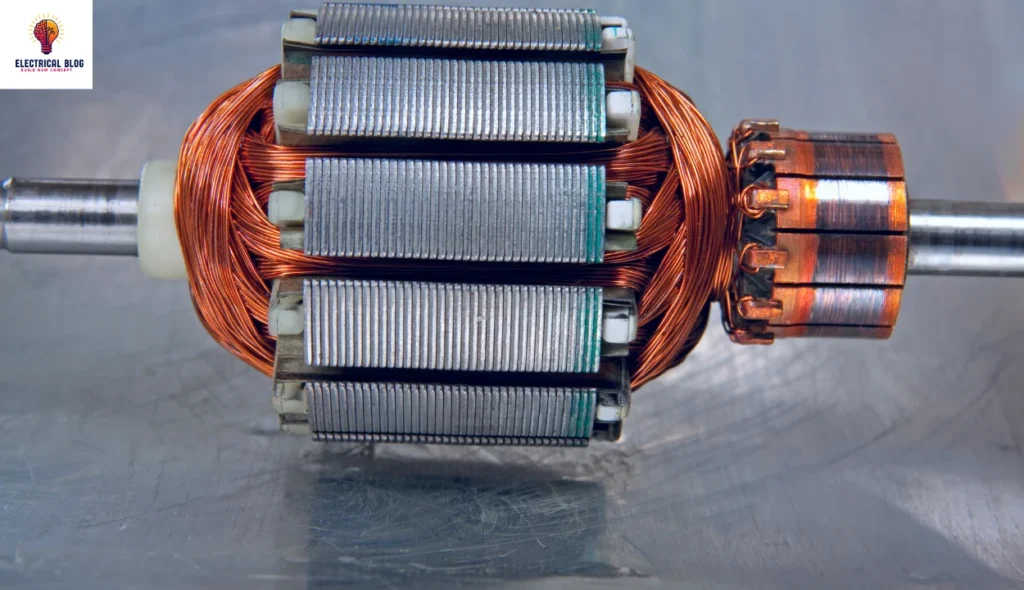
Characteristics of Universal Motors
Efficiency of Universal Motor
Smaller universal motors have an efficiency of about 30%, while larger universal motors can reach 70-75%, making them more energy efficient for high-power applications.
Speed Load Characteristics of Universal Motor
The speed-load characteristics of a universal motor show that its speed is highest at no load and lowest at full load. To achieve the required performance, gear trains are often used to adjust the speed. These characteristics apply to motors operating on both AC and DC power sources.
Universal Motor Speed Control
To avoid a universal motor running at dangerous speeds under no load, different control methods are used. One approach is to build the motor into a device where it always operates under a load. This setup is preferred for small applications that require the motor to be directly connected to the system it drives.
Other types of speed control include using a gear train to reduce the actual speed, the resistance method, and the centrifugal mechanism. Another effective method is field tapping, which adjusts the desired motor value for stable operation.
Variations of Universal Motors
Shunt Winding
Shunt winding was experimented with in the 19th century, but it failed due to poor commutation. Unlike series-wound designs, engineers attempted various combinations of embedded resistance, inductance, and antiphase cross-coupling to improve performance. However, these adjustments did not provide long-term success.
Although shunt-wound motors had the property of self-starting, they were later replaced by induction motors and automatic starters due to their availability and efficiency. Despite being a preferred option for some applications, their limitations made other motor types more practical for widespread use.
Repulsion Start
A repulsion-start motor provides high torque but has a more complex design. Its rotors are similar to universal motors, but the brushes are only connected to each other. This wound motor type is efficient but requires careful handling for optimal performance.
Applications of Universal Motors
Universal Motors is widely used in portable tools like drilling machines and polishers due to their high speed and compact size.
They power household devices such as table fans, hair dryers, and kitchen appliances, making daily tasks more convenient.
Industrial applications include grinders and blowers, where strong performance and reliability are essential.
Conclusion
Universal motors are highly versatile due to their ability to operate on both AC and DC power. Their small size, fast speed, and strong torque make them perfect for many uses. You can find them in household items like hairdryers and kitchen gadgets. They are also great for industrial tools, including drilling machines, grinders, and blowers.
Their speed control methods include gear trains, resistance control, and field tapping. These techniques help manage performance. They ensure safe operation under various loads. Series-wound universal motors are the best choice. They are efficient and reliable, especially in tough conditions. Although shunt winding and repulsion-start variations have been studied, series-wound motors still stand out.



