Introduction
The 2N2222A is a commonly used NPN transistor in amplifier and switching applications. This small-signal transistor is specially designed for very high frequency (VHF) use, where its reliability shines. Built with silicon material, it is considered a normal transistor in its class. Often, this transistor is used in a variety of circuits, making it a go-to component for engineers in everyday designs. Its versatility is what makes it a staple in the world of electronics.
What is a 2N2222A transistor?
The 2N2222A transistor is a widely used NPN transistor and BJT, commonly applied in switching and amplifying tasks. It is designed for low power or less power operations, supporting low to medium current and medium voltage needs. This transistor works reliably at high speeds, making it perfect for various practical applications. From personal experience, it is one of the most dependable components for prototyping and educational use.
Internally, the 2N2222 has a single P-doped layer embedded between two N-doped layers. It consists of three terminals—Base, Emitter, and Collector—which are clearly shown in its circuit symbol. The constant DC collector current rating is up to 800 mA, supporting circuits that need low to medium current handling. Additionally, its high transition frequency of 250 MHz, 10 ns delay time, 225 ms storage time, 60 ms fall time, and 25 ms rise time ensure excellent speed and switching behavior.
It comes in a compact TO-92 package, making it easy to integrate into small layouts. There are many alternative 2N2222A transistors like BC636, BC549, BC639, 2N2369, BC547, 2N3055, 2N3906, 2N3904, and 2SC5200. Some equivalent 2N2222 transistors include 2N3904 (PNP), 2N2907 (PNP), 2N3906 (PNP), S9014, BC637, BC148, MPS2222, 2N4403, PN2222, KTN2222, and KN2222—all useful depending on your design needs. You can also read field-effect transistor.
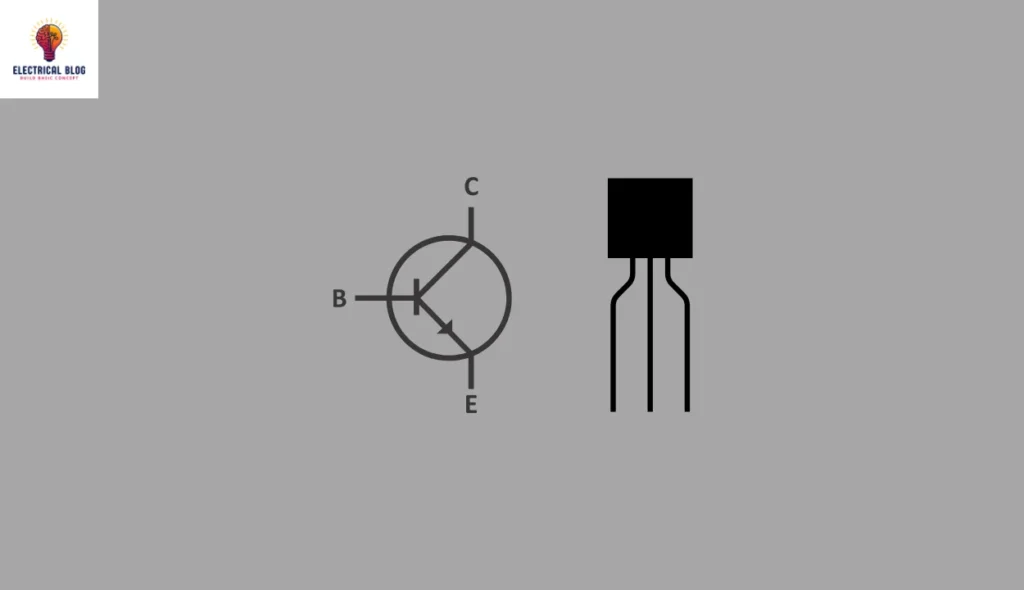
2N2222A transistor symbol
2N2222A Transistor Pin Configuration
The 2N2222A transistor has a pin configuration with three pins, each having a specific functionality in a circuit.
Pin1 (Collector) is the first pin, acting as an output pin that carries current to the output load from the transistor.
Pin2 (Base), the second pin, works as a control pin, managing current flow between the emitter and base, ensuring proper control in circuit operation.
Pin3 (Emitter) is the third pin, responsible for draining out the complete current from the transistor, which is shown clearly in its symbol.
Features and Specifications of the 2N2222A Transistor
The 2N2222 is an NPN transistor known for its reliable polarity and versatile use in electronic applications.
It has a type of termination as a through-hole, making it suitable for breadboard-friendly circuit designs.
The configuration of the pin is simple, with the number of pins being three, clearly marked for ease of connection.
The voltage rating between the collector terminal and emitter is 50 V when the base terminal is open.
The voltage from the emitter to the base terminal is 6 V with the collector terminal open.
The voltage from collector to base reaches 75 V when the emitter terminal is open.
The current gain in DC mode is around 100, which is great for amplifying voltage, current, and power.
The DC collector current capacity of this transistor is 800 mA, ideal for medium-load circuits.
It is packed in a TO-92 package, making it compact and suitable for small-space designs.
The power dissipation limit is 1 W, which supports decent performance in controlled environments.
The maximum base current is 5 mA, keeping the input side safe and effective.
The input capacitance is 25 pF, while the output capacitance is 8 pF, which helps with fast switching.
The fall time is just 60 ns, and the turn-on time is as quick as 25 ns, ensuring rapid signal response.
Various configuration modes, such as common emitter (CE), common collector (CC), and common base (CB), allow flexibility in usage.
These configurations are extremely helpful and can be easily adapted to different circuit requirements.
I’ve used this NPN transistor in several DIY kits, and it always delivers strong amplification performance under various conditions.
How to Use the 2N2222A Transistor?
One of the best beginner-friendly projects is a touch switch circuit using the 2N2222A transistor. This simple circuit helps control a relay instead of just an LED and resistor, making it easier to operate any connected appliance or load. The essential components include an input DC supply of 6V, two 2N2222 transistors, and resistors of 330Ω, 200kΩ, and LED-1.
This circuit works as a Darlington pair, where the first transistor amplifies the gain and the second transistor multiplies it. This results in high gain, so even a small current is enough to activate the LED. You can try operating it with 6V, 9V, or 12V, using 330Ω, 390Ω, or 470Ω resistors accordingly. If replacing the LED with a relay, match it with the input voltage.
A variable resistor of 200KΩ helps regulate the sensitivity of the circuit. When the touchpoints are touched, current supplies trigger the LED or relay action. I’ve personally used this method in DIY projects like lamps, locks, doors, and even safety boxes—it’s reliable and fun to build.
Characteristics of the 2N2222A transistor
The transistor is known for its stability, and its complete power limit should not exceed 500 mW, which makes it reliable in most circuit designs.
It offers maximum handling with a frequency capacity of 250 MHz, suitable for high-speed switching applications.
The maximum tolerance of the transistor is 60V across the terminals, especially between the base and collector, ensuring it withstands moderate voltage conditions.
With a 10 mA collector current and 10 V input, the DC current output reaches approximately 75 mA, making it highly efficient in signal amplification tasks.
Advantages of the 2N2222A transistor
The 2N2222A transistor is commonly used in many electronic circuits, especially where switching applications are needed.
It is capable of handling high-magnitude currents, which makes it more efficient than similar transistors.
This transistor easily switches the load current, supporting up to 800 mA, which is quite high for its category.
It is an ideal choice for applications like linear amplifiers, where stability and performance are essential.
Its small size allows for compact placement on circuit boards, making the design more efficient.
The lesser weight feature also makes it suitable for portable or space-limited designs.
It offers high-voltage gain, improving signal strength without the need for extra circuitry.
The low source voltage requirement helps in building energy-efficient devices.
One of the key benefits is its low cost, making it accessible to students and professionals alike.
The longer life of this transistor means it lasts longer in continuous operation.
From my personal projects, this transistor has always proven to be reliable under varying circuit conditions.
Disadvantages of the 2N2222A transistor
The 2N2222A transistor is quite sensitive, and its performance often depends on temperature, which can affect circuit stability.
One limitation is that its input impedance is low, which might not suit every high-impedance application.
Due to its small size, detecting faults becomes difficult, especially in compact or dense circuit layouts.
It’s hard to replace the transistor during repair, as unsoldering can be tricky without damaging the board.
It does not function efficiently in certain switching roles, such as relays or traditional electrical and mechanical switches.
From my personal experience, careful handling is crucial when working with such sensitive components in real-world designs.
Applications of the 2N2222A transistor
The 2N2222 is an NPN transistor that works very well in places where switching and amplifying currents are needed.
It is quite similar to the BC547, but it handles 800 mA of collector current and 652 mW of power dissipation, which is perfect for driving larger loads.
This transistor is great for switching high-current loads, making it a solid choice for practical circuit work.
It can switch on and off different appliances automatically, which is useful in smart electronics projects.
Its quick response and fast response time make it ideal for PWM (pulse width modulation) tasks.
You’ll often find it used in automation and embedded projects where reliable switching is critical.
I’ve used it in several audio preamplifiers and sensor circuits for boosting signals effectively.
It’s also great in audio amplifier stages, thanks to its ability to amplify voltage, current, and power.
The 2N2222 can be used to switch several loads simultaneously, a benefit in multi-output systems.
You will find this transistor in RF circuits, where stability and fast operation are essential.
It is often used in Darlington pairs to boost gain further for sensitive applications.
In my experience, motor drive circuits like VFDs (variable frequency drives) also benefit from their power.
It’s a strong choice for rectifier circuits and DC inverters, delivering reliable performance.
The 2N2222 also works well as an amplifier, especially for maximizing gain.
With Darlington pair transistors, you can achieve maximum current from the emitter terminal to the collector efficiently.
This transistor stands out in projects where signal clarity and load management are essential.
Whether for basic circuits or advanced designs, its flexibility and strength make it a favorite in my toolkit.
Conclusion
The 2N2222A transistor is a powerful and reliable NPN transistor that plays a key role in both basic and advanced electronic circuits. Its ability to handle high current, amplify signals, and respond quickly makes it suitable for a wide range of applications—from switching loads, PWM, and audio circuits to automation and embedded projects. With advantages like small size, low cost, high voltage gain, and longer life, it stands out as a go-to component for engineers and hobbyists alike. Despite a few disadvantages like sensitivity to temperature and low input impedance, its performance, durability, and versatility far outweigh the limitations, making it an essential part of any electronics toolkit.