Introduction
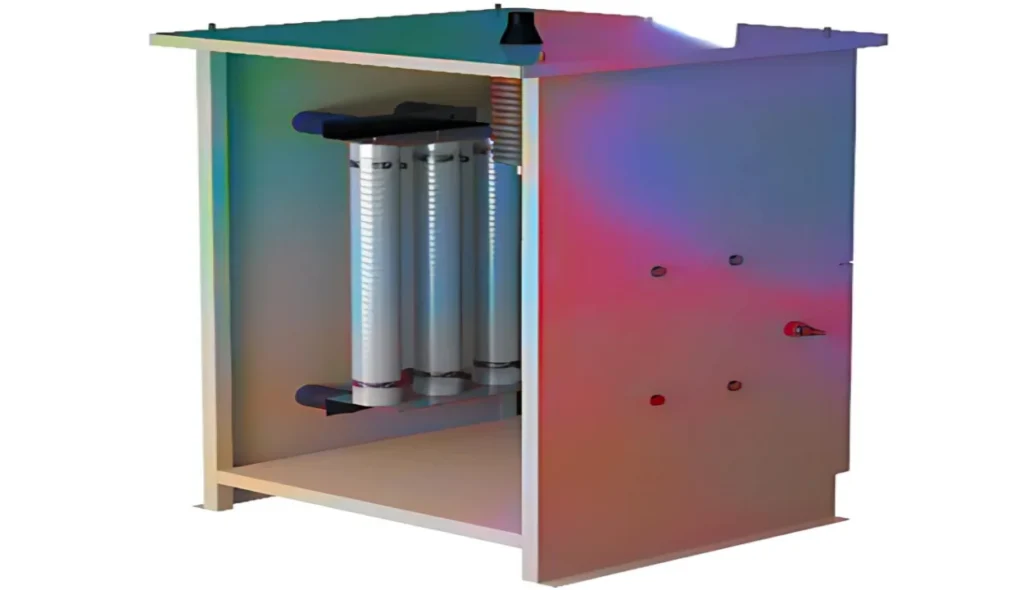
A Neutral Earthing Resistor (NER) is an essential component used in electrical systems to control fault currents and enhance safety. It connects between the system’s neutral point and ground, limiting excessive current flow during faults. By doing so, Neutral Earthing Resistors prevent severe damage to equipment, improve system stability, and reduce the risk of arc flash hazards. They are widely used in power systems across industries like power generation, distribution networks, and industrial facilities to ensure smooth and secure operations.
What is a Neutral Earthing Resistor?
A Neutral Earth Resistor (NER) is a crucial element in electrical systems that ensures safety by reducing the risk of severe fault currents. When a short circuit occurs, such as a line-to-ground event, the NER limits the short-circuit current to a reasonable level. This is particularly important in medium-voltage and high-voltage networks to avoid dangerously high currents that could cause equipment damage and compromise stability.
By placing a resistor between the neutral and ground, the system gains improved stability and minimizes the possibility of damage. This approach is common in systems where direct earthing would pose a risk to operators and critical equipment. The NER is pivotal in conserving the power grid’s reliability, ensuring the use of motors, generators, and other devices remains secure under event-based disruptions. You can also read variable resistor.
How Neutral Earthing Resistors Work
A Neutral Earth Resistor (NER) is vital in protecting the power system by controlling leakage current. It efficiently prevents severe damage by ensuring safe bounds of current in both normal and fault situations.
The NER limits fault current by introducing a resistor in the circuit, helping to maintain system integrity. This setup avoids electrical fires and shields infrastructure and electrical equipment from harm.
During faults, the NER generates a voltage drop that aids in fault detection. This allows for identifying and isolating the affected section, improving operational safety in the electrical system.
Careful configuration of the NER is required, ensuring it meets voltage and requirements for the system. It operates continuously, maintaining a safe level of current under normal conditions and reducing disruption during events.
By regulating current flow, the NER protects motors, generators, and other key devices. This controlled resistance method effectively maintains system protection, guaranteeing stability and performance. You can also read ballast resistor.
Purpose of a Neutral Earthing Resistors (NERs)
A Neutral Earthing Resistor (NER) helps lower the risk of ground faults by limiting the short-circuit current. This protects key equipment like transformers, generators, and switchgear from overcurrents that could cause serious damage.
To prevent overvoltages, the NER controls leakage during faults, avoiding insulation leakage that may weaken the system’s protection. This step is crucial for maintaining strong insulation in the network.
The NER improves protection coordination by enhancing relay protection. It supports leak detection and ensures fast isolation of faults to reduce potential damage.
By reducing energy loss, the NER minimizes the impact of unexpected ground leak issues. This prevents catastrophic failures and effectively stops severe equipment damage.

Types of Neutral Earthing Resistors
Low-Resistance Earthing Resistors
Low-Resistance Earthing Resistors are designed to limit fault currents in medium-voltage networks. They provide a brief yet effective solution that ensures safe operation by reducing the risk of short-circuit currents. These resistors act as a safeguard to protect equipment from sudden failures.
High-Resistance Earthing Resistors
High-Resistance Earthing Resistors are ideal for low-voltage systems, effectively reducing the risk of flash overvoltage. By controlling short-circuit current, they help maintain stability while preventing severe fault occurrences. This design is common in environments where ongoing protection is necessary.
Permanently Connected Earthing Resistors
These resistors remain connected to the neutral point at all times, providing consistent defense against ground fault currents. They are widely used in industrial applications with sensitive equipment to ensure stable system impedance. This type is crucial for preventing electrical short circuits.
Portable and Temporary Earthing Resistors
Portable Earthing Resistors offer movable solutions for maintenance or temporary power setups. In cases where fixed resistors are impractical, they provide flexible protection by connecting only during faults and disconnecting afterward to limit damage. This method efficiently handles infrequent electrical issues.
Design Considerations of Neutral Earthing Resistors
The resistance value of a Neutral Earthing Resistor (NER) is carefully chosen to match the desired fault current level. Depending on the system, this can vary from a few ohms to several hundred ohms to ensure stable performance and safety.
The NER must be engineered to manage the energy dissipated during a fault. This may involve enduring brief surges lasting seconds or sustained exposure to ensure reliable operation without damage.
For safety in dangerous surroundings, the NER is often enclosed in waterproof and explosion-proof enclosures. This protection ensures the system remains secure and operational under extreme conditions.
Applications of Neutral Earthing Resistors
Power Generation Stations use Neutral Earthing Resistors. These resistors control fault currents. This helps keep the system stable and the equipment safe.
In distribution networks, these resistors manage electrical faults. They reduce downtime and protect transformers.
Industrial facilities rely on them to maintain smooth operations by preventing electrical disturbances.
Renewable Energy Systems need these resistors. They help manage changing power conditions and boost reliability.
At electric substations, neutral earthing resistors are crucial for preventing short-circuit damage.
Motors and drive systems benefit from these resistors by ensuring controlled fault current flow.
In railway electrification, better electrical fault protection helps to keep train operations safe and efficient.
Oil and gas platforms utilize these resistors to reduce risks from electrical faults in offshore environments.
In Mining Operations, they protect equipment from ground faults, ensuring continuous operation.
Marine vessels use these resistors to prevent electrical hazards in their power systems.
Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) integrate Neutral Earthing Resistors to manage energy surges and faults.
HVAC systems employ these resistors to avoid electrical failures during heating and cooling cycles.
Data centers depend on neutral earthing resistors to minimize disruptions caused by electrical faults.
Hospitals utilize these resistors to ensure a stable power supply for critical medical equipment.
Building Automation Systems use these resistors to maintain electrical stability. They also protect sensitive devices.
Advantages of Using Neutral Earthing Resistors
Controlled fault currents prevent excessive electrical surges, reducing the risk of severe damage to the system.
Enhanced Safety provides better protection for people and equipment. It does this by managing electrical faults effectively.
Improved System Stability maintains a steady power supply during fault conditions, reducing interruptions.
Protection of equipment minimizes the risk of damage to transformers, generators, and other key devices.
Reduced Arc Flash Hazard lowers the chance of dangerous electrical explosions, improving workplace safety.
Minimized Damage During Ground Faults ensures that the system remains functional with minimal repairs needed.
Improved Ground Fault Detection allows faults to be identified quickly, enabling faster maintenance.
Compliance with standards ensures the electrical system meets safety and regulatory requirements.
Cost-effective solutions reduce downtime, minimize damage, and extend equipment lifespan efficiently.
Conclusion
Neutral Earthing Resistors play a crucial role in ensuring electrical system safety, stability, and efficiency. By controlling fault currents, enhancing safety, and protecting equipment, they prevent severe damage and costly repairs. They improve ground fault detection and reduce arc flash hazards. This helps ensure compliance with standards. So, they are a cost-effective choice for many industries. Investing in Neutral Earthing Resistors is smart. They help keep power systems reliable and protect important infrastructure.