Introduction
In the world of electricity, disc-shaped insulators act as silent guardians, keeping the current separated from what could be shocking. Like stones in a river, these champions manage transmission and distribution across lines, systems, and landscapes, working tirelessly to maintain safety. Their role ensures that lights keep buzzing, appliances stay humming, and every neighborhood functions smoothly.
Different kinds and types of these marvels—from heavy-duty tamers to pollution-resistant components—bring strength, durability, and adaptability. They handle tasks under tension, withstand high voltage, and serve equal importance in network applications, whether for vehicles or large towering structures. As blog writers reveal the hidden secrets, these electrical guardians prove how vital they are in powering the world smoothly.
What are Disc Insulators?
A disc insulator is an important part of electrical systems that carry power through overhead lines. These insulators provide support for conductors, hold their weight, and keep them safely apart with proper insulation. Used on towers, poles, and other structures, they work in transmission, distribution, suspension, and strain setups to protect the flow of energy.
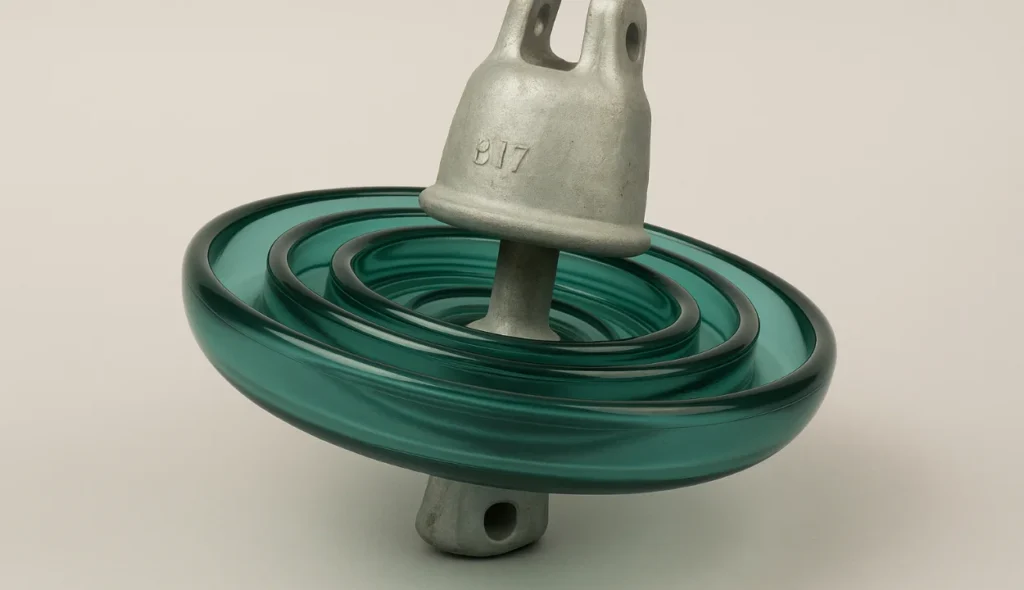

Suspension Type Insulators
Suspension-type insulators are designed to suspend the conductor from a tower or pole, giving strong support under varying loads. They handle the weight of the line along with wind and ice, even when forces act vertically and push downwards. These insulators are hung in a string, and the metal fittings at the end help them securely carry the conductor.
Strain Type Insulators
Strain-type insulators are specially made for termination points or corners where a conductor changes its direction. These insulators can handle tensile forces and keep the full length steady, whether mounted horizontally or placed at an angle. The conductor is attached at each end of the string, firmly anchoring it to a tower or pole in dead-end tension setups.
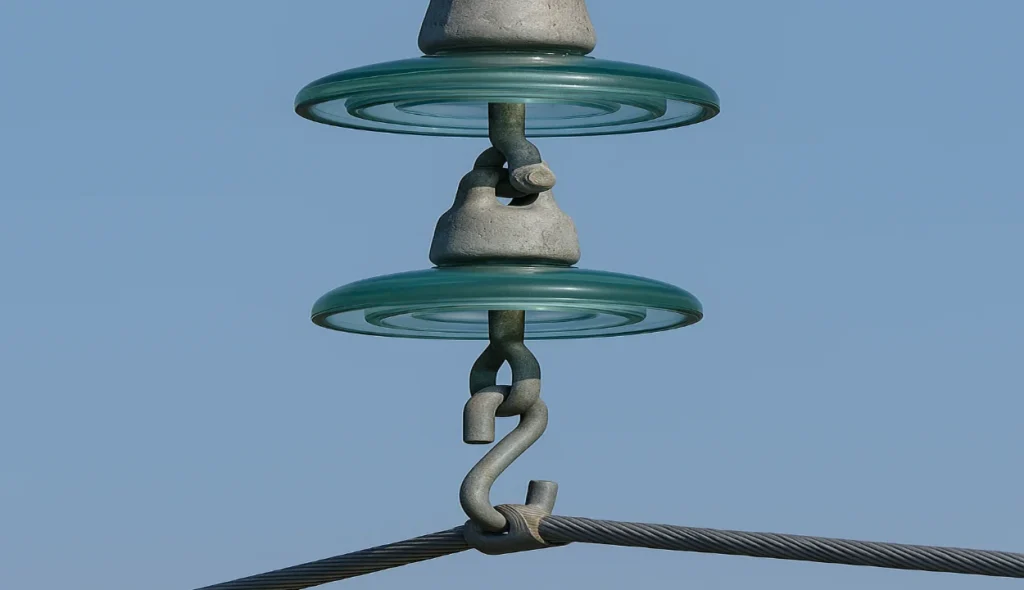

Types of Disc Insulators
Disc insulators are built from different materials like porcelain, toughened glass, rubber, silicone, or polymer to suit varied needs. They can be arranged in a series of discs or bells, forming a string or complete set joined with metal fittings. Each grooved surface increases the distance for leakage, improving the insulating properties of these composite designs.
Porcelain Insulators
Made from ceramic materials, these disc insulators are valued for their electrical and mechanical properties. They provide durability in tough environmental conditions and are common in many regions.
Glass Insulators
Produced from toughened or tempered glass, they are lightweight, resistant to corrosion, and reliable in coastal or high pollution areas. Their good insulating properties make them dependable.
Composite Insulators
Built with silicone rubber, polymer, and fibreglass rods, these designs are hydrophobic, repelling water and contaminants. They remain stable in humidity and perform well in polluted conditions.
Polymer Insulators
Using polymeric blends like EPDM, ethylene, and propylene diene monomer, they offer strength, stability, and resistance to ageing and UV exposure. These insulators are modern and versatile.
Cap and Pin Insulators
This design links each disc with a metal cap and pin arrangement, giving extra strength and the ability to handle heavy loads. They ensure better mechanical performance through reinforcing connections.
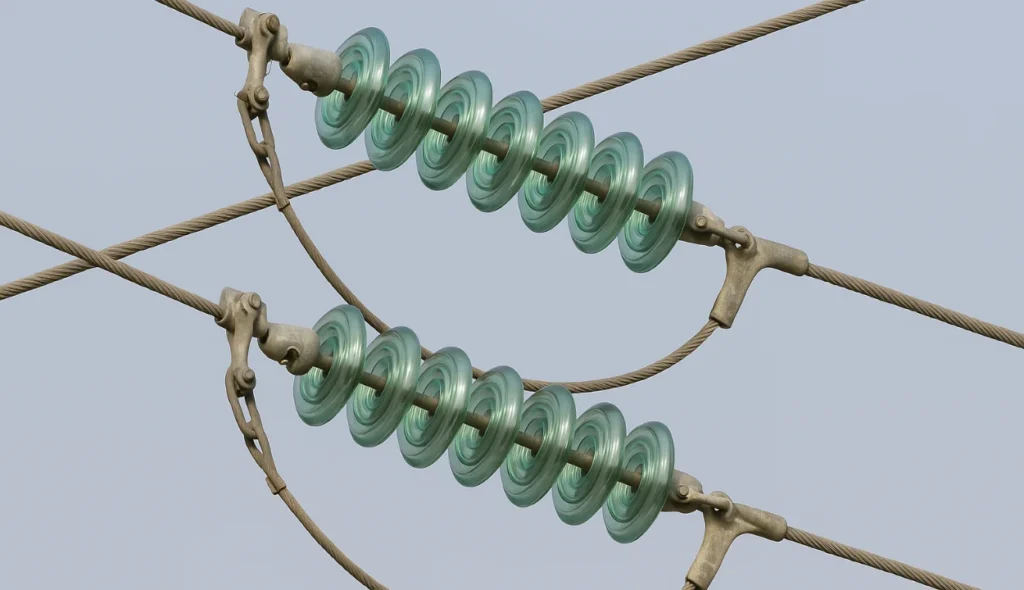
Applications of Disc Insulators
Overhead and Transmission Use
Disc insulators are placed on overhead lines to support conductors and insulate them during power transmission. Their design ensures reliable performance over long distances, protecting both the electricity flow and connected equipment.
Substations and Busbars
In substations, these insulators keep busbars and other components safely apart. By providing proper isolation, they maintain high levels of safety and stability in electrical installations.
Industrial and Generation Plants
Industrial areas and plants rely on disc insulators to handle voltage stresses. Whether in generation sites or heavy-duty installations, their ability to protect sensitive equipment makes them indispensable.
Distribution to Consumers
Finally, distribution lines carrying electricity to consumers depend on these insulators. They provide the support needed to ensure safe and continuous delivery, bridging the gap between large networks and end-users.
Advantages of Disc Insulators
Strong Mechanical Build
Disc insulators are valued for their mechanical strength, able to handle stresses from wind, ice, and other external factors. This makes them dependable for long transmission service even in extreme conditions.
Reliable Electrical Function
These insulators prevent leakage and reduce losses, ensuring efficient flow of power across high electrical networks. Their performance in varied operating environments helps maintain steady energy delivery.
Resistance to Harsh Environments
Built to endure UV radiation, shifting temperatures, moisture, and pollution, they work reliably under challenging conditions. In my experience, this durability extends their life and reduces unexpected downtime.
Lightweight and Easy Handling
Modern polymer types are lightweight, compact, and simple to handle. Their design eases transportation and installation, cutting effort during setup while keeping systems safer.
Low Maintenance Needs
With minimal maintenance, these insulators avoid frequent replacements. Their long service life reduces costs and limits interruptions, keeping projects running smoothly even in demanding environments.
How to Choose the Best Disc Insulators
When selecting a disc insulator, I always remind engineers to look beyond the market options and think about the real application needs. The decision should balance safety, reliability, and long-term performance in electrical systems. Key factors like voltage requirements, environmental conditions, and material selection often determine whether the choice meets expected standards. Practical tips, such as evaluating quality certifications, help you choose wisely, ensuring your investment aligns with technical expectations.
Understand the Voltage Requirements
When working with a disc insulator, the first step is to check the voltage level of the electrical system. Always select an option that meets or even exceeds the required rating, since this directly impacts safety and performance. Different designs and materials are made for specific ranges, ensuring the right insulation that fits your application perfectly.
Evaluate Environmental Conditions
When selecting a disc insulator, it is vital to take into account the environmental conditions where it will be installed. Factors like temperature variations, humidity levels, pollution, and UV radiation exposure can affect long-term performance. Always choose an option designed to withstand these environments, with a proven track record that ensures reliable insulator use in demanding settings.
Evaluate Environmental Conditions
When selecting a disc insulator, it is vital to take into account the environmental conditions where it will be installed. Factors like temperature variations, humidity levels, pollution, and UV radiation exposure can affect long-term performance. Always choose an option designed to withstand these environments, with a proven track record that ensures reliable insulator use in demanding settings.
Consider Mechanical Strength
A disc insulator must offer enough mechanical strength to withstand loads in areas exposed to high wind speeds, ice, and other external stresses. In my experience with overhead lines and transmission projects, ignoring this factor often leads to unexpected failure. Always assess how the insulator performs under stress, ensuring it endures challenging field conditions without compromise.
Check Quality Standards
When you choose a disc insulator, make sure it complies with standards and regulations set by trusted organizations. A reliable product is usually tested, certified, and has undergone strict testing for both electrical and mechanical performance. High-quality insulators meeting these requirements give confidence that the insulator will work effectively in real conditions.
Conclusion
From overhead lines to substations and distribution networks, Disc insulators remain vital components in electrical systems. Their strength, resistance, and reliability provide safe and efficient power transmission across high-voltage applications. With a lightweight design, long longevity, and the ability to handle mechanical and environmental factors, they deliver clear advantages. For professionals and stakeholders, understanding types and making informed decisions ensures proper support, durable insulation, and better outcomes in complex applications.