Introduction
Auto generators are vital. They convert mechanical energy into electrical energy. They provide backup power during outages and in off-grid areas. These generators start automatically during a power failure. They ensure an uninterrupted electricity supply in all applications. This includes residential, commercial, and industrial uses. Auto generators come in different types. Diesel generators are common. They are durable and fuel-efficient.
Standby generators are vital in modern homes. They power essential appliances during blackouts, like refrigerators, HVAC systems, and lights. Auto generators protect businesses in commercial buildings. They prevent costly downtime and data loss. In factories, auto generators keep vital processes, like hospital systems, running. They ensure no disruptions to things like manufacturing lines.
This blog aims to help readers choose the right auto generator. It will explain how they work and what affects their performance. This includes power capacity, fuel type, and maintenance needs. By exploring options, readers can find the best solution for their specific needs. These can be residential, commercial, or industrial. This ensures they are ready for any power loss.
What are auto generators?
Auto generators are backup power systems. They automatically provide electricity during a power outage. They convert mechanical energy into electrical energy. This ensures a steady power supply. An auto generator works on electromagnetic induction. A diesel, natural gas, or propane engine spins a coil in a magnetic field to generate electricity.
Auto generators have an automatic transfer switch (ATS). It monitors the power from the main grid. If a failure is detected, the ATS activates the generator. It transfers the load to the backup system. Once grid power is restored, the ATS switches back, and the generator powers down.
Differences Between Manual and Automatic Generators
The key difference between manual and automatic generators is how they transfer power. A manual generator needs a person to start it. They must also flip a switch to transfer power from the grid to the generator. An automatic generator starts on its own. It needs no human help. This provides convenience and ensures continuous power during outages.
Automatic generators are better for homes and businesses needing constant power. Use manual generators where some downtime is okay, and people can watch them.
Types of Auto Generators
Diesel Generators
Diesel generators are one of the most common types of auto generators used for backup power. These systems run on diesel fuel. They are very reliable for both residential and industrial use. Diesel generators are efficient. They can provide continuous power for long periods. They come in various forms. They include portable, silent, and standby generators. Each suits different power needs.
Natural Gas Generators
Natural gas generators operate by using natural gas or propane as a fuel source. These generators are environmentally friendly due to lower emissions compared to diesel generators. They are ideal for homes and businesses with natural gas lines. They provide a continuous, abundant fuel supply. This type of generator is quieter and needs less upkeep than diesel models.
Solar-Powered Generators
Sunlight is converted into electrical power by solar panels in a solar-powered generator. These systems are eco-friendly. They rely entirely on renewable energy. Solar generators are usually for small-scale use. But advances are making them better for larger needs. They are ideal for off-grid setups and places with a limited fossil fuel supply.
Hybrid Generators
Hybrid generators use multiple power sources, like diesel and solar. This makes them more flexible. These systems aim to cut fuel use and emissions. They are cost-effective and eco-friendly. Hybrid generators are versatile. They switch energy sources based on availability and demand. They are, therefore, appropriate for a range of uses.

Key Components of Auto Generators
Engine
The engine is the primary component that drives the autogenerator. It converts fuel, like diesel or natural gas, into mechanical energy. This energy is then used to produce electricity. The size and type of the engine directly impact the generator’s output power and efficiency.
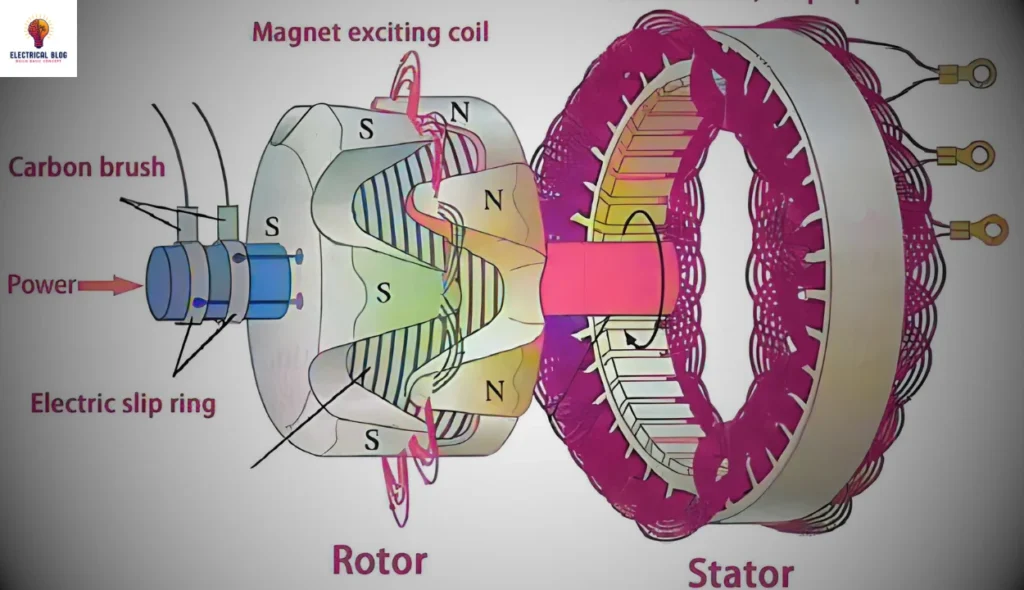
Alternator
The alternator, or generator head, converts the engine’s mechanical energy into electrical energy. It does this through electromagnetic induction. A well-maintained alternator is crucial for reliable power output.
Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS)
An Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS) swaps between the main power and the generator. It does so seamlessly. The ATS detects a power outage. It then activates the generator and transfers the load to it. This maintains an uninterrupted power supply. The ATS switches back on after the main power is restored.
Voltage Regulator
The voltage regulator keeps the generator’s output at a steady voltage. It ensures the generator delivers steady power. This protects equipment from damaging voltage fluctuations.
Battery and Control System
The battery and control system are vital. They start the generator and monitor its performance. The battery starts the engine. The control system monitors voltage, current, and engine temperature for efficient operation.
Working principles of auto generators
The Process of Automatic Power Generation
Auto generators provide power during outages. They auto-generate electricity when the main supply fails. The system typically runs on fuel, like diesel or natural gas. It powers an internal engine. The engine converts mechanical energy into electrical energy using an alternator. The alternator generates AC power. It powers the connected electrical systems.
When power is restored, the generator stops. The load switches back to the mains supply. This ensures no interruption in power delivery. This process relies on key components. One is the Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS). It controls the switch from mains to generator power.
Switching Between Mains and Generator Power: The Role of ATS
The ATS is key to an auto generator. It detects any power outages in the mains supply. When the ATS senses a power failure, it sends a signal to start the generator. Once the generator is stable, the ATS switches the load from the mains to it. This ensures a smooth power transition. The ATS watches the mains. When the primary power is restored, it switches back to mains power and safely shuts down the generator.
Choosing the Right Auto Generator
Choosing the right auto generator requires careful thought. You must consider several key factors to ensure it meets your needs. Below are the most important factors to consider:
Size and Power Output
The size of the generator and its power output are crucial. For homes, a smaller generator (5-20 kW) can power appliances and essential systems. For commercial or industrial use, you need a larger generator. It must have a higher output, often over 100 kW, to handle bigger electrical loads.
Fuel Type
The right fuel type for your auto generator affects its cost and efficiency. Common fuel types include diesel, natural gas, propane, and even gasoline. Diesel is popular for its reliability and efficiency. It is used in industrial generators. Natural gas is a cleaner alternative with a steady supply.
Efficiency
Generator efficiency impacts both fuel consumption and operational costs. High-efficiency generators use less fuel and run longer. They are ideal for both homes and industries. Choosing the most efficient generator saves money in the long run. This is key for commercial or industrial use, where the generator runs for long periods.
Residential vs. Commercial vs. Industrial Needs
For home use, you need a smaller generator. It must power essential systems like heating, cooling, and lighting. In contrast, commercial and industrial generators are built for higher loads. They are often needed in large facilities or construction sites. These industrial models have stronger designs for high-demand, continuous use.

Installation Best Practices
When installing an auto generator, follow the best practices. They are vital for long-term performance and safety. Some important guidelines include:
Proper Sizing: Ensure the generator is correctly sized based on power needs. Oversized or undersized generators can lead to inefficiencies or overload issues.
Location: Install the generator in a well-ventilated, protected area. This avoids overheating and exposure to the elements. It is important to maintain at least 5 feet of clearance around the generator.
Professional Installation: Always use a licensed electrician for complex wiring in any residential, commercial, or industrial setting.
Fuel Source: The fuel line (natural gas, propane, or diesel) must connect securely. This prevents leaks or pressure drops that can affect performance.
Maintenance schedules and tips for keeping generators running efficiently.
Regular maintenance is key to your generator’s lifespan and efficiency.
Preventive maintenance: Schedule routine inspections to check for wear and tear. Oil, coolant, and fuel levels should be inspected and topped off if necessary.
Performance Monitoring: Install devices to monitor your generator’s performance in real time. This facilitates the early detection of any possible problems.
Load Testing: Regular load tests ensure the generator can provide the required power in emergencies. This is especially important for industrial generators that power large facilities.
Cleaning and Lubrication: Keep the generator clean and lubricate all moving parts. This reduces wear and enhances efficiency.
Advantages of Auto Generators
Convenience: One of the main advantages of auto generators is their convenience. They automatically detect power outages and start supplying electricity without any manual intervention. This allows homes and businesses to continue their activities during outages.
Reliability: Reliability is another significant benefit. Auto generators provide a steady power source. They keep essential appliances running during grid failures. For companies that cannot afford downtime, this is essential. It’s also key for homes that rely on medical or heating equipment during extreme weather.
Fuel Efficiency: Modern auto generators are designed with fuel efficiency in mind. They utilize advanced technology to optimize fuel consumption, reducing operational costs over time. This efficiency leads to longer runtimes and fewer refuels. So, they are a practical choice for extended outages.
Disadvantages of Auto Generators
Initial Cost: The upfront investment for auto generators can be substantial. The cost of buying and installing a generator can deter some consumers. This includes permits and electrical upgrades. In the long run, they might save money. However, the high upfront cost is a significant concern.
Maintenance: Like any machine, auto generators need regular upkeep. It keeps them running well. Routine checks, oil changes, and parts replacements raise ownership costs. When the generator is most needed, neglecting maintenance might result in a breakdown.
Environmental Concerns: Environmental impact is another consideration. Many auto generators run on fossil fuels, contributing to carbon emissions. As cleaner technologies improve, eco-conscious consumers debate traditional generators’ environmental impacts.

Environmental Impact of Auto Generators
Emissions and Fuel Consumption
Auto generators mainly run on fossil fuels. They emit pollutants that harm the air and contribute to climate change. Diesel and gasoline generators release harmful pollutants. They include carbon dioxide (CO2), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and sulfur dioxide (SO2). These emissions harm air quality and threaten human and wildlife health. Also, auto generators can use a lot of fuel, especially during long use. This worsens their environmental impact.
Solutions for Eco-Friendly Use
To reduce the harm from autogenerators, we can use eco-friendly solutions.
Hybrid Models: Hybrid auto generators use traditional fuels and renewable energy, like solar. This integration reduces reliance on fossil fuels and lowers emissions significantly. These models use renewable energy. They improve fuel efficiency and cut costs over time.
Renewable Energy Sources: Using wind or solar energy to power generators can greatly reduce fuel use and emissions. For example, solar panels can provide clean power to support generators at peak demand times.
Regular Maintenance: Proper maintenance of auto generators boosts efficiency and reduces fuel use. Regular checks and tune-ups keep the engines running smoothly. This minimizes harmful emissions.
Conclusion
Auto generators have many benefits. They provide reliable power during outages. A key benefit of these automatic generators is their ability to start up when a power failure occurs. This eliminates the need for manual intervention. This is vital for homes and businesses that need power for essential services. An automatic generator keeps appliances running. It keeps food in fridges, secures systems, and lets businesses work. Also, modern auto generators are built to be eco-friendly. They have features that boost fuel efficiency and cut emissions. So, they are good options for backup power.
When choosing a generator, consider your specific power needs. Knowing your wattage needs will help you choose a generator. Your decision will depend on your home’s or business’s size, the number of appliances you want to run at once, and whether you need a temporary or permanent solution. Also, evaluate whether an automatic or manual switch generator better suits your needs. Some environments may prioritize immediate power over manual control. By assessing these factors, you can choose a generator. It will meet your power needs and offer peace of mind during outages.