Introduction
Ignition systems are vital to any vehicle. They affect performance and efficiency. The choice of ignition technology can affect a vehicle’s fuel ignition. This, in turn, affects power, fuel use, and maintenance. The options are a transistorized ignition system (TIS) or capacitive discharge ignition (CDI).
In modern car engineering, TIS and CDI systems are two advanced ignition methods. The transistorized ignition system uses transistors to control the spark. It provides better timing and reliability than traditional systems. This tech suits apps needing steady performance, especially at low engine speeds. So, it is popular for everyday vehicles and motorcycles.
A capacitive discharge ignition system uses a capacitor. It quickly releases stored energy to the spark plug, making a much stronger spark. CDI systems can discharge very quickly. So, they are ideal for high-performance uses. These include racing and off-road vehicles, where quick, high-energy sparks are essential. In this article we will explore transistorized ignition system vs cdi.
Understanding Ignition Systems
In internal combustion engines, ignition systems are essential for starting the combustion process. They create the spark to ignite the fuel-air mix in the engine’s cylinders. This produces the energy needed to power the vehicle. An engine needs a working ignition system to start and run well. Without it, performance and reliability would suffer.
Basic Functionality of Ignition Systems
An ignition system primarily works by generating a high-voltage spark to ignite the fuel-air mixture in each cylinder. This process begins with the ignition coil, which converts low battery voltage into a much higher voltage. This high voltage is then directed to the spark plugs at the right moment, which produces a spark that ignites the mixture. The timing and strength of this spark are critical. Any deviation can cause engine misfires or reduced power. This affects the engine’s performance and efficiency.
Importance of Efficient Ignition
An efficient ignition system boosts fuel efficiency, engine reliability, and emissions control. Precise timing ensures the fuel-air mixture ignites at peak combustibility. This maximizes power and minimizes unburned fuel. This efficiency leads to better fuel economy and helps reduce harmful emissions. Also, a reliable ignition system reduces engine wear. It lowers maintenance needs and extends the engine’s life.
Transistorized and capacitive discharge systems are efficient ignition systems. They offer better control and reliability, especially at high engine speeds. So, they are ideal for various vehicles. A robust ignition system is vital. It ensures engine performance, boosts fuel efficiency, and enables a reliable drive.
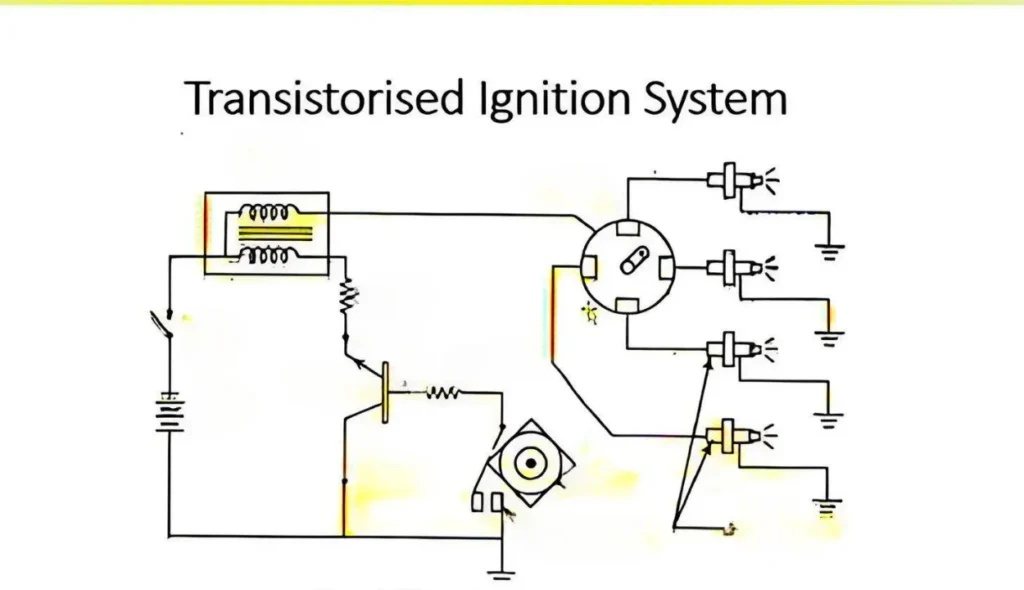
What is a Transistorized Ignition System?
A Transistorized Ignition System (TIS) is an advanced electronic ignition. It uses a transistor as a switch to control the high-voltage current to the spark plugs. Unlike traditional ignition systems that use mechanical points, TIS relies on solid-state electronics. This results in a more efficient and precise ignition. This improvement enhances engine performance, reduces maintenance needs, and provides better fuel efficiency.
Structure and Working Principle of Transistorized Ignition
The transistorized ignition system uses electrical parts to control the ignition spark’s timing and strength. When the ignition switch is turned on, the battery supplies voltage to the system. The ignition control module manages the timing by controlling a switch. It allows high-voltage current to flow from the ignition coil to the spark plug. It creates the spark to ignite the fuel-air mix in the engine’s cylinders. This ensures smooth combustion and better performance.
Components of the Transistorized Ignition System
Transistor Switch: Acts as the core switch in the ignition system. It controls the flow of current, allowing for faster switching and precise spark timing.
Battery: Supplies low-voltage power to the ignition system.
Ignition Coil and Spark Plug: The coil boosts the voltage from the battery, and the spark plug generates a spark, igniting the fuel-air mixture.
Ignition Control Module: It manages the timing of the transistor switch. It ensures that the spark occurs at the right moment for optimal combustion.
Working Mechanism
The transistorized ignition system boosts weak signals from the ignition module. It then creates a high-energy spark. Here’s how it works:
Signal Amplification: The control module sends a signal to the transistor switch. It amplifies the signal to allow a larger current to flow to the ignition coil.
Controlled Timing: The system controls when the spark occurs. It does this by accurately switching the transistor on and off. This optimizes the ignition timing based on engine speed and load.
Ignition Process: The coil transforms the battery’s low voltage to a high voltage, which is directed to the spark plug to ignite the fuel.
Types of Transistorized Ignition Systems
Basic Transistorized Ignition: Uses a single spark for each ignition event. It is reliable for everyday driving conditions and provides consistent ignition timing.
Advanced Transistorized Ignition with Multiple Spark Technology: It boosts combustion efficiency, especially at low engine speeds. Multiple sparks ensure a better burn of the fuel-air mixture. This enhances fuel efficiency while decreasing emissions.
What is a Capacitive Discharge Ignition (CDI) system?
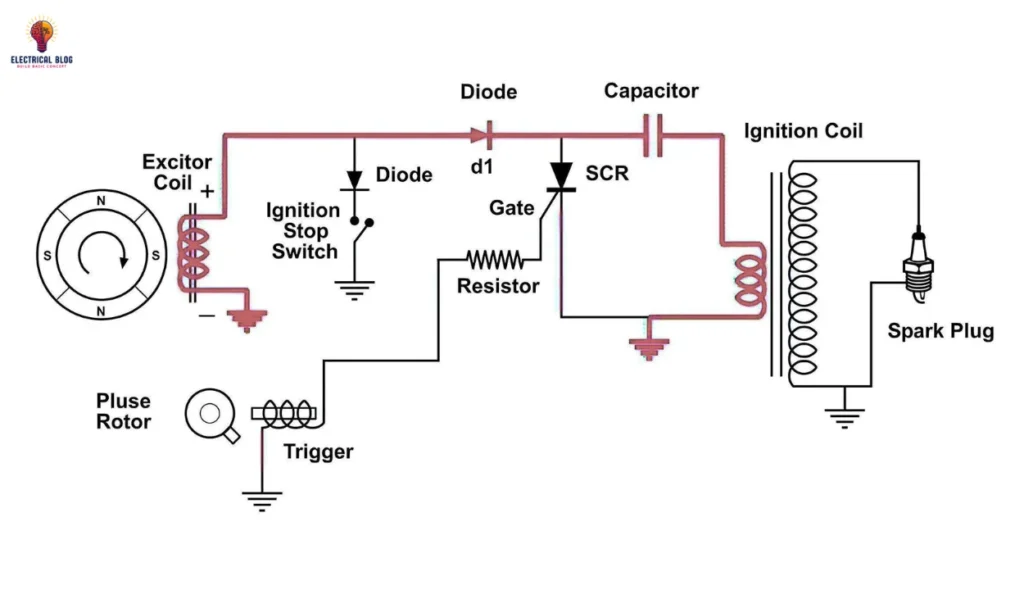
A Capacitive Discharge Ignition (CDI) system is an electronic ignition. It is common in high-performance engines and motorcycles. It is favored for its ability to produce a powerful, rapid spark, which is ideal for high-speed, high-compression engines. This system charges a capacitor to a high voltage. It then discharges it to ignite the air-fuel mixture, causing efficient combustion. CDI systems are great for engines that need quick, repeated sparks without overheating.
Components of a CDI system
A CDI system comprises several key components:
Capacitor: Stores electrical energy and releases it rapidly to generate a high-intensity spark.
Ignition Coil: Steps up the capacitor’s voltage to a level sufficient to create a spark at the spark plug.
Triggering Mechanism: This component, usually points or a sensor, controls when the capacitor discharges.
Spark Plug: Receives the high-voltage discharge and creates the spark needed to ignite the engine’s air-fuel mixture.
Working Mechanism of CDI
In a Capacitive Discharge Ignition system, the capacitor charges to a high voltage (typically around 300-400 volts). When the trigger mechanism signals the system, the capacitor discharges. It sends a high-voltage pulse through the ignition coil. The ignition coil then boosts the voltage further, delivering a powerful spark across the spark plug. This discharge process happens quickly. It enables efficient ignition in high-performance engines. It also reduces wear on the parts due to its speed.
Types of CDI systems
There are two primary types of CDI systems:
Analog CDI: Uses simple circuitry to control spark timing. These systems are generally less expensive but offer limited control over spark timing.
Digital CDI: Uses a microcontroller to manage timing, allowing for more precise adjustments. Digital CDI systems can adjust spark timing based on engine speed. This improves fuel efficiency and performance.
Key Differences Between Transistorized Ignition System (TIS) and Capacitive Discharge Ignition (CDI)
Spark Energy and Intensity
In transistorized ignition system vs cdi, the spark energy in a CDI system is typically higher and more intense than in a TIS. CDI systems rapidly release stored energy from a capacitor. This produces a high-voltage, short-duration spark. It is very effective for igniting lean fuel mixtures or in conditions needing a strong ignition. TIS uses lower voltage but a longer spark duration. It is better for reliable ignition and smoother idle performance.
Timing and Spark Duration
TIS has more precise timing control. It uses transistors. They allow better modulation of spark duration. The result is improved fuel economy and a more refined acceleration. CDI systems ignite quickly, but their timing is less adjustable. This limits their flexibility at low RPMs. TIS is often preferred for apps with variable engine speeds that need adaptable spark timing.
Voltage Levels
CDI operates at much higher voltage levels than TIS. CDI systems typically boost voltage to over 400V before discharging to the spark plug. TIS generally operates around 12V and gradually ramps up the voltage. The CDI’s high voltage gives a quick, powerful spark. It’s great for high-performance engines. The TIS’s gradual voltage ramp-up supports a stable, long-lasting spark. It’s best for everyday engines.
Application Suitability
Application suitability differs significantly between the two systems. CDI is preferred in high-performance and racing vehicles. The quick, intense spark helps at high RPMs and with leaner fuel mixtures. TIS is more common in daily-use vehicles where smooth ignition and fuel efficiency are prioritized. CDI’s rapid spark output can help maximize power but may lead to less efficient fuel consumption under normal driving conditions.
Maintenance and Durability
TIS is more reliable long-term. It has lower voltage stress on components, meaning less wear and tear. CDI systems are powerful. But, they may need more frequent component replacements. Higher operational stress can shorten their lifespan in high-use settings. TIS is durable and has a longer spark duration. This makes for a smoother engine performance, ideal for standard automotive engines.
Cost Efficiency
Cost efficiency is another key factor. CDI systems often have high setup costs due to their complex, high-voltage components. Over time, TIS tends to be more economical, given its durability and reduced need for high-cost component replacements. CDI systems are more expensive but have better performance. They are worth the investment for high-performance applications. TIS is the budget-friendly option for typical vehicles.
Advantages and Disadvantages of the Transistorized Ignition System
Advantages of the Transistorized Ignition System
More fuel-efficient: The transistorized ignition system maintains a stable spark. It works well, even if there is fuel or debris on the spark plug. This spark improves combustion. It boosts fuel efficiency and performance in most standard vehicles.
Stable spark with fewer high-voltage requirements: The transistorized system, compared to other ignitions, needs less high-voltage energy to create a consistent spark. This makes it ideal for engines that don’t require intense spark power, such as those found in everyday vehicles. The system’s design ensures consistent ignition without voltage degradation, even in less-than-ideal conditions.
Lower maintenance and longer lifespan. The transistorized ignition system has no moving parts. So, it is less likely to wear out. This durability reduces the need for frequent tune-ups, extending the lifespan of the ignition system. This advantage not only saves time but also results in long-term cost savings for vehicle owners.
Disadvantages of the Transistorized Ignition System
Limited spark intensity: A transistorized ignition system’s spark lacks the high intensity needed for very high-speed or high-power uses. This limits the system’s use in racing vehicles. They need maximum power for speed.
Slightly slower response compared to CDI: The transistorized ignition system is efficient. But it responds a bit slower than the CDI system, which is designed to produce a rapid, high-intensity spark. This slight delay may affect performance in demanding conditions. But it is negligible in standard vehicle uses.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Capacitive Discharge Ignition (CDI)
Capacitive Discharge Ignition (CDI) systems are common in modern, high-performance engines. Knowing the pros and cons of this ignition system can help you choose wisely for your vehicle.
Advantages of CDI
High-Intensity Spark: A key benefit of CDI systems is their high-intensity spark. This feature makes CDI perfect for performance apps. It ensures better ignition of the air-fuel mix, especially under high load or racing conditions.
Faster Ignition Timing: CDI systems are designed to provide faster ignition timing. This means they can initiate combustion more quickly, allowing for improved engine response at higher RPMs. The quick ignition boosts engine performance and efficiency. This is vital in racing.
Disadvantages of CDI
Higher Maintenance: CDI systems have many benefits. But, they can require more maintenance. The components may experience significant stress, especially under extreme operating conditions. Over time, this stress can lead to increased wear and necessitate more frequent repairs or replacements.
Cost Considerations: CDI systems are usually more expensive than traditional ignition systems. The advanced technology and components involved in CDI can increase the initial investment. Also, CDI may reduce fuel efficiency in low-power uses. Its complex energy management causes this.
Choosing the Right Ignition System: TIS or CDI?
When choosing an ignition system for your vehicle, consider these key factors. The two common types are TIS and CDI. They are Transistorized Ignition Systems and Capacitive Discharge Ignition, respectively. Each has its unique advantages and is suited to different applications.
Vehicle Type Consideration
The choice between TIS and CDI often depends on the type of vehicle. CDI systems are common in motorcycles and high-performance vehicles. They provide a high-intensity spark for fast ignition, which is crucial for racing. On the other hand, TIS is used in standard cars. It provides reliable ignition and enough performance for daily driving.
Performance Goals
It is crucial to match the ignition system with your vehicle’s performance goals. For maximum power and efficiency, especially in racing, CDI is usually better. It can deliver faster ignition timing. If you want reliable performance for general use, a TIS can meet your needs. It is simpler than a CDI.
Budget and Maintenance Preferences
Cost implications are another vital consideration. CDI systems usually need a higher initial investment. Their complexity may increase maintenance needs. In contrast, TIS tends to be more economical upfront and easier to maintain over time, making it a sensible choice for those on a tighter budget. Evaluating these factors will help you find the best system for your financial and performance goals.
Conclusion
Transistorized Ignition Systems (TIS) and Capacitive Discharge Ignition (CDI) differ mainly in design and use. CDI systems provide a high-intensity spark. So, they are ideal for high-performance vehicles, like motorcycles and race cars. In transistorized ignition system vs cdi, TIS offers reliable ignition suitable for standard automobiles, delivering sufficient power for daily driving without the complexities associated with CDI systems.
When selecting an ignition system, consider the type of vehicle you have. For performance-oriented applications where power and responsiveness are paramount, opt for CDI. However, if you prioritize cost-effectiveness and ease of maintenance, TIS may be the better choice. Ultimately, evaluating your performance needs and budget will guide you to the right decision.
Those who want to boost their vehicle’s capabilities should explore various ignition systems. Knowing the nuances of each system can help tune and customize your engine for specific driving demands.
Read more: Types of 5477 Transistors


