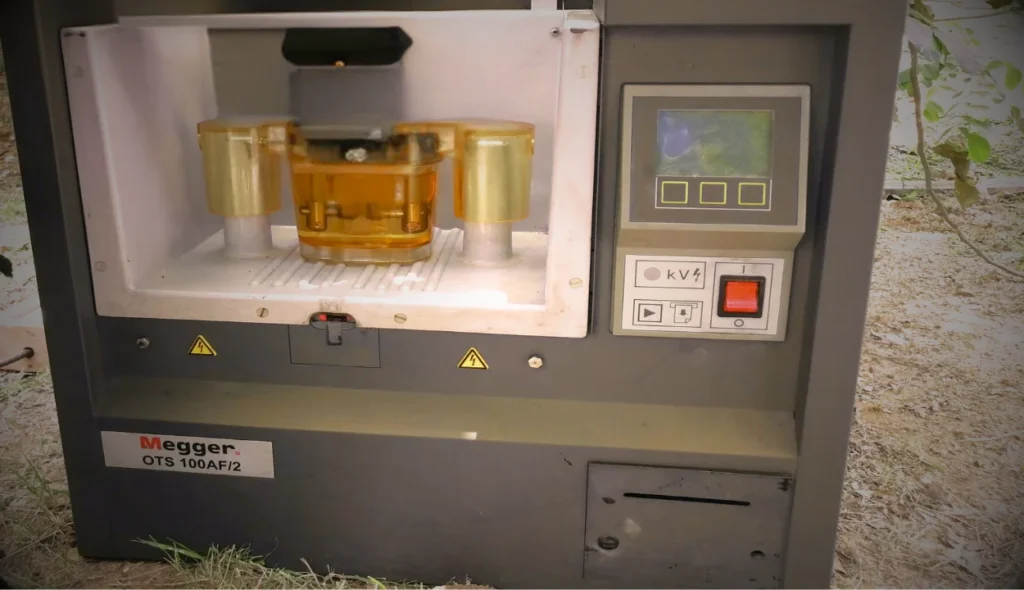
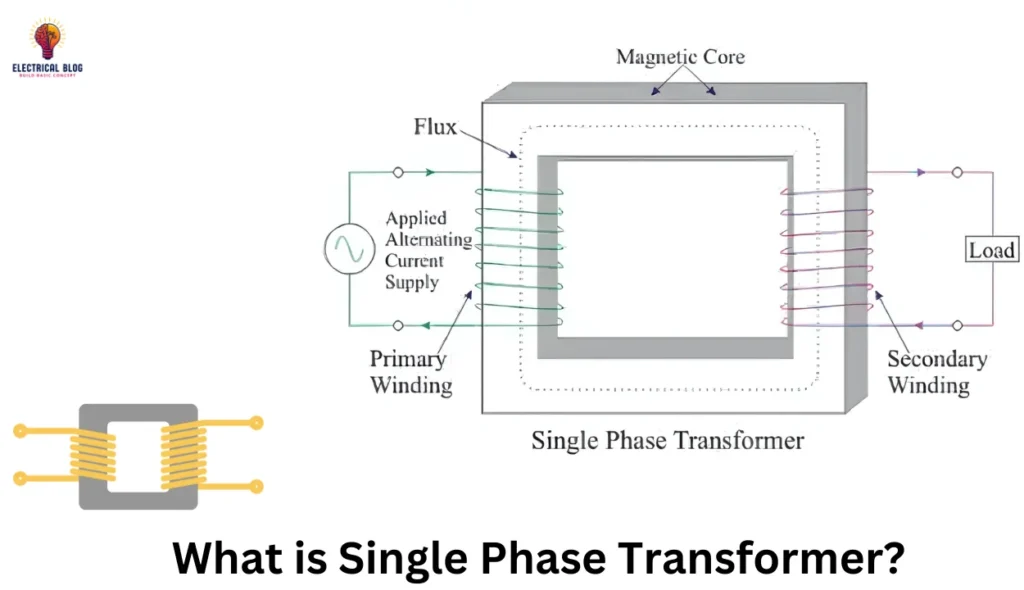
Introduction
Transformer oil is vital for electrical equipment. It insulates and cools. Its main job is to prevent electrical discharges in the transformer. It does this by maintaining high dielectric strength and cooling the system. It cools the system by dissipating heat generated during operation. The quality of transformer oil is essential. It ensures transformers operate reliably and last long.
One of the key methods to evaluate the quality of transformer oil is the Breakdown Voltage (BDV) test. This test measures the oil’s dielectric strength. It applies increasing voltage until the oil fails. A high BDV means good insulation. A low BDV signals oil contamination or decay. Regular transformer oil BDV test checks transformer oil health. It finds failure risks and ensures safe equipment operation.
What is BDV (Breakdown Voltage)?
The Breakdown Voltage (BDV) of transformer oil is its maximum voltage. It’s the point at which the oil’s insulating properties fail, causing a current to flow. It is a key factor. It ensures the transformer operates reliably under high voltages. A low BDV means the oil is contaminated. This can harm the transformer’s insulation and raise the risk of failure.
Minimum BDV Standards
IEC standards say transformer oil must have a minimum BDV of 30 kV. This threshold applies regardless of the voltage rating of the transformer, whether it is 11 kV, 22 kV, or 132 kV. Testing transformer oil for BDV ensures it is fit for use. It boosts reliability and lowers the risk of transformer failure.
What is the transformer oil BDV test?
The transformer oil BDV test is a diagnostic test. It measures the insulating strength of transformer oil. Transformer oil insulates and cools power transformers. Moisture, dirt, and gases can accumulate in the oil over time. This reduces its insulating capacity. The transformer oil BDV test checks the oil’s high-voltage endurance. It tests whether it can withstand high voltage without breaking down.
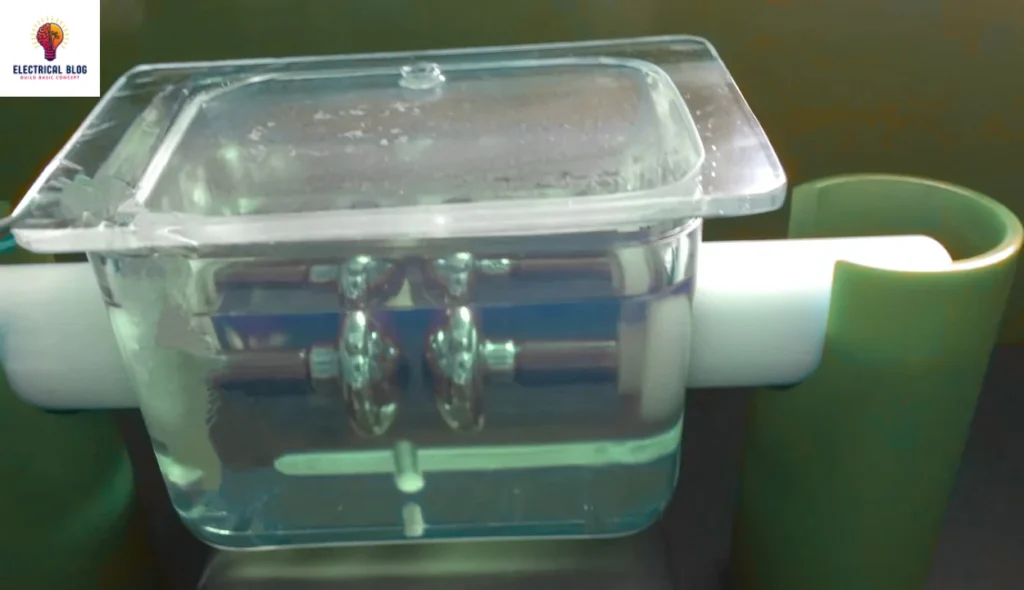
Importance of BDV Testing for Transformer Oil
Transformer oil keeps high-voltage electrical components insulated from each other. If the oil loses its insulating properties, it can cause short circuits. This may lead to catastrophic transformer failures. Regular BDV testing helps us find issues early. It keeps power transformers safe and reliable. It is critical to keep the BDV value within limits to avoid electrical breakdowns.
Key benefits of conducting a transformer oil BDV test include:
Identifying oil contamination: Contaminants lower the oil’s dielectric strength, risking failure.
Ensuring operational safety: Maintaining proper insulation prevents accidents and operational downtime.
Cost savings: Timely detection of oil degradation allows for preventive maintenance. This reduces costly repairs or transformer replacements.
The Principle of Transformer Oil BDV Testing
The BDV test measures the dielectric strength of the transformer oil. The test applies an increasing voltage to the oil sample until it fails to insulate. The breakdown voltage is when the oil loses its insulation. It then allows the electrical current to pass through, causing a failure. The test results show the oil’s effectiveness as an insulator. A higher breakdown voltage means better insulation.
The test is conducted using a BDV tester, which consists of an oil cup with electrodes submerged in the oil. The voltage is slowly increased until the oil breaks down. This allows current to pass through the electrodes. The test is repeated several times to ensure accuracy. Impurities in the oil may cause variability in the results.
Procedure for Transformer Oil BDV Testing
Step-by-Step Process
Preparation: Clean and dry the oil test cup, gauge, stirring rod, and cover glass to avoid contamination. Ensure the transformer oil sample is cooled to approximately 27°C before testing.
Sampling: Take a sample of the transformer oil from the designated sampling port, ensuring the port is cleaned and dried. Rinse the oil cup with the sample oil three times to remove any residues.
Setting Electrode Distance: Adjust the electrode gap in the oil cup to 2.5 mm using a standard gauge. Slowly pour the transformer oil into the cup until the oil level is at least 10 mm above the electrodes.
Let the Oil Settle: Allow the oil to stand for 15 minutes to remove any air bubbles that may have been introduced during the pouring process.
Increase Voltage: Turn on the BDV tester and begin increasing the voltage at a controlled rate of 3-5 kV per second. Keep increasing the voltage until the oil breaks down. This will cause the overcurrent trip mechanism to activate and disconnect the power supply.
Clear Carbon Residue: Use a glass stirring rod to gently clean any carbon particles from the electrodes after each breakdown. This ensures accurate measurements for subsequent tests.
Repeat the Test: The test should be repeated six times, discarding the result from the first test. The final BDV value is the average of the remaining five tests.
Transformer oil BDV test report format
Example of a Transformer oil BDV Test Result
Six breakdown tests were conducted on a transformer oil sample, with the following breakdown voltage results:
Test 1: 52 kV
Test 2: 42 kV
Test 3: 47 kV
Test 4: 40 kV
Test 5: 43 kV
Test 6: 40 kV
The average breakdown voltage for this oil sample is calculated as:
Average BDV = 52+42+47+40+43+40/6 =44kV
This result, 44 kV, represents the final BDV value of the insulating oil sample. A breakdown voltage above 30 kV typically indicates that the transformer oil is in good condition.
Key Considerations for BDV Testing
Clean Equipment: Any contamination in the oil cup or on the electrodes can affect the accuracy of the test results. Thorough cleaning is essential.
- Remove Air Bubbles: Let the oil settle for 15 minutes before the test. This will remove air bubbles that could cause premature breakdown.
Correct Electrode Gap: Ensure the distance between the electrodes is precisely set to 2.5 mm to avoid skewed test results.
Repeatability: Run multiple tests. Then, average the breakdown voltage. This accounts for variations from impurities and other factors.
Using a Transformer Insulating Oil BDV Tester
Transformer oil BDV testers, like the GTD1001D, test breakdown voltage. They are very precise and accurate. Below is a step-by-step guide to using the tester:
Power Connection: Connect the tester to an AC 220V power supply. Make sure the ground terminal is connected to a standard ground wire.
Install the Oil Cup: Carefully install the oil cup and adjust the electrode spacing to 2.5 mm.
Turn on the tester: Switch on the power. The voltmeter should display 00.0 before starting the test.
Pressure Reduction: Reduce the voltage before initiating the test, as failure to do so will prevent the tester from operating.
Fill the Oil Cup: Pour the transformer oil into the oil cup, ensuring it is filled above the electrodes, and let it stand to remove any air bubbles.
Test Execution: Press the boost switch to gradually increase the voltage. The tester will automatically cut off the voltage supply when the oil breaks down.
Record Results: After each test, note the breakdown voltage value displayed on the meter.
Repeat Tests: Allow the oil to stand for 5 minutes between tests and repeat the test six times to obtain accurate results.
Specifications of the Transformer Insulation Oil BDV Tester
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Output Voltage | 0~80 kV (0-100 kV) |
| THVD | < 1% |
| Pressure Rate | 0.5~5.0 kV/s |
| Booster Capacity | 1.5 kVA |
| Measurement Accuracy | ±2% |
| Supply Voltage | AC 220 V ±10% |
| Power Frequency | 50 Hz ±2% |
| Power Consumption | 200 W |
| Temperature Range | 0~45℃ |
| Humidity Range | < 85% RH |
| Dimensions | 410×390×375 mm |
| Weight | ~32 kg |
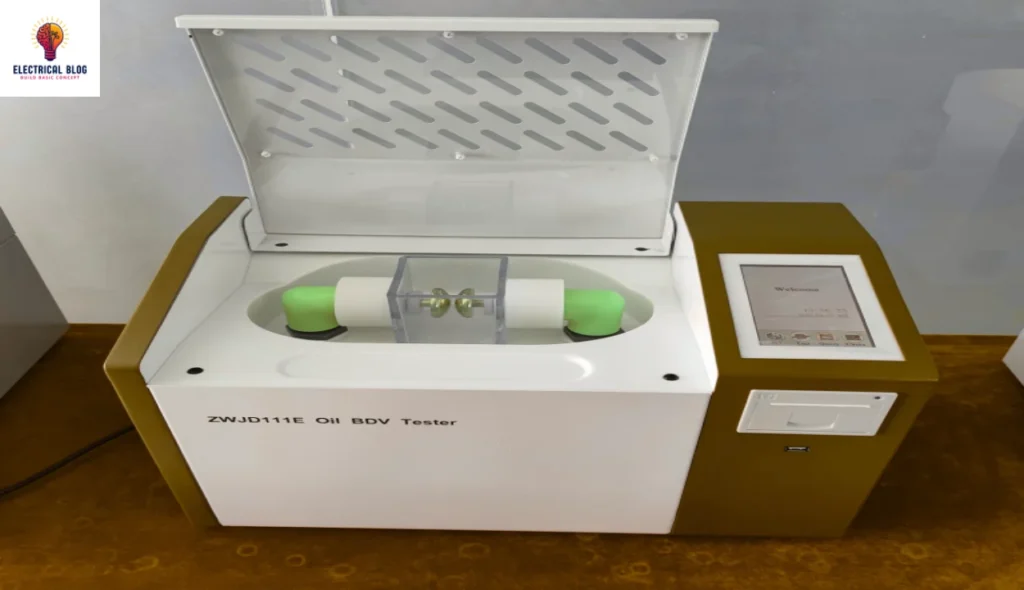

Transformer oil BDV test standards
Various standards provide guidance on acceptable BDV values for transformer oils. The most widely followed standards include IEC 60156 and ASTM D1816.
New transformer oil: A BDV value of 30 kV or higher is considered good for new oil.
In-service transformer oil: Transformer oil that has been in use should typically maintain a BDV value of 20 kV or higher. Anything below this threshold needs further analysis and action. This may include oil purification or replacement.
These values benchmark the oil’s dielectric strength. They help to determine if the oil is still usable.
Factors Affecting the BDV of Transformer Oil
Several factors can influence the BDV value of transformer oil. Knowing these factors helps us find issues in transformer insulation and fix them.
Moisture Content
Water is one of the most common contaminants in transformer oil. Even trace amounts of moisture can significantly reduce the oil’s dielectric strength. Moisture in the oil results from factors such as poor seals, condensation, or even leakage. Keeping the oil dry is essential to maintaining high BDV values.
Particles and sediments
Solid impurities, such as dirt, dust, and metallic particles, can also reduce the BDV of transformer oil. These particles act as conductive paths, facilitating a breakdown in the insulating properties of the oil. Proper filtration and regular maintenance can help mitigate the impact of the particles.
Dissolved Gases
Gases, particularly oxygen, and other reactive gases, can form as a result of transformer operation or oil oxidation. Dissolved gases can degrade the oil’s dielectric properties and reduce the BDV. Regular oil analysis helps us track and control gas content.
Age and Oxidation
As transformer oil ages, it undergoes chemical changes due to oxidation and exposure to high temperatures. These changes result in a breakdown of the oil’s molecular structure, leading to reduced BDV values. Older oil is more prone to contamination and loss of dielectric strength, which is why regular testing is essential.
Improving Transformer Oil BDV
If the BDV test shows that the transformer oil is too low, action must be taken to restore its insulating properties. The following steps can help improve the BDV of transformer oil:
Oil Filtration
Filtration removes solid particles and contaminants from the oil. Regular oil filtration helps maintain oil purity, thereby improving its BDV.
Dehydration
Removing moisture from transformer oil is one of the most effective ways to enhance its dielectric strength. Vacuum dehydration processes can be used to reduce the water content in the oil, improving the BDV significantly.
Degassing
Removing dissolved gases from transformer oil can also improve its dielectric strength. Degassing equipment is often used in tandem with filtration systems to restore oil quality.
Oil Replacement
If transformer oil is badly degraded or too contaminated to purify, replace it. Using fresh, high-quality oil restores the transformer’s insulation and longevity.
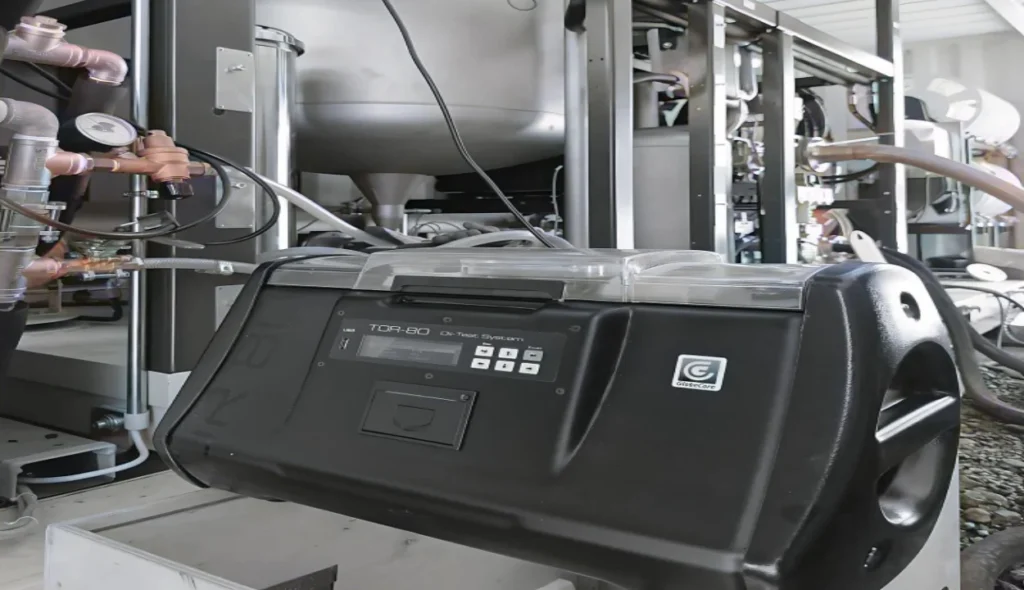

Types of Oil BDV Testers
Single-Cup Oil BDV Tester
This type of tester uses a single sample of oil for the dielectric strength test. It is best suited for rapid assessments and situations where smaller volumes of oil are available for testing.
Three-Cup Oil BDV Tester
A more advanced version, the three-cup tester allows for multiple tests at once or in quick succession. This gives a better analysis of the oil sample.
Six-Cup Oil BDV Tester
The six-cup tester is more efficient. It’s ideal for large operations that need to test multiple oil samples at once. It is commonly used in large transformer facilities.
Key Features of the BDV Tester
Advanced Microprocessor Control: The BDV tester is controlled by a high-capacity microprocessor. It ensures stable, reliable operation. This control mechanism enables precise test management and reduces human error.
Wide Range Watchdog Circuit: A built-in watchdog circuit ensures consistent, reliable test results. It eliminates the risk of system freezes or malfunctions.
Multiple Testing Standards: The instrument meets international standards: ASTM D1816, ASTM D877, and IEC 156. It can adapt to different testing environments and user preferences. Additionally, custom testing methods can be programmed for specialized requirements.
Oil Spill Prevention Design: The tester uses a special glass mold. It prevents oil spills and outside interference. This ensures accurate, reliable test results.
High-Voltage Sampling: The high-voltage terminal’s unique design lets test values bypass analog circuits. This reduces measurement errors and improves accuracy. This innovative sampling design improves the tester’s overall performance.
Robust Protection Features: The BDV tester has protections against overcurrent, overvoltage, and short circuits. This not only enhances user safety but also protects the equipment from potential damage during testing.
Portable and Easy to Use The lightweight and portable design makes the tester suitable for both laboratory and field use. Its compact structure allows for easy transportation and convenient testing in various environments.
Conclusion
The transformer oil BDV test is a vital diagnostic tool for evaluating the condition of transformer oil. Regular testing and transformer maintenance helps us. It checks the oil’s insulation, finds contamination, and ensures the safe operation of power transformers. High BDV values reduce the risk of transformer failure. They also extend equipment life and ensure a reliable power supply. Additionally, improving oil quality will boost transformer performance and reliability. Proactive measures include filtration, dehydration, and degassing.
To ensure peak transformer performance, keep the oil’s BDV value within limits. Also, maintain it regularly to fix issues before they become critical.
Read more: Full form of DP