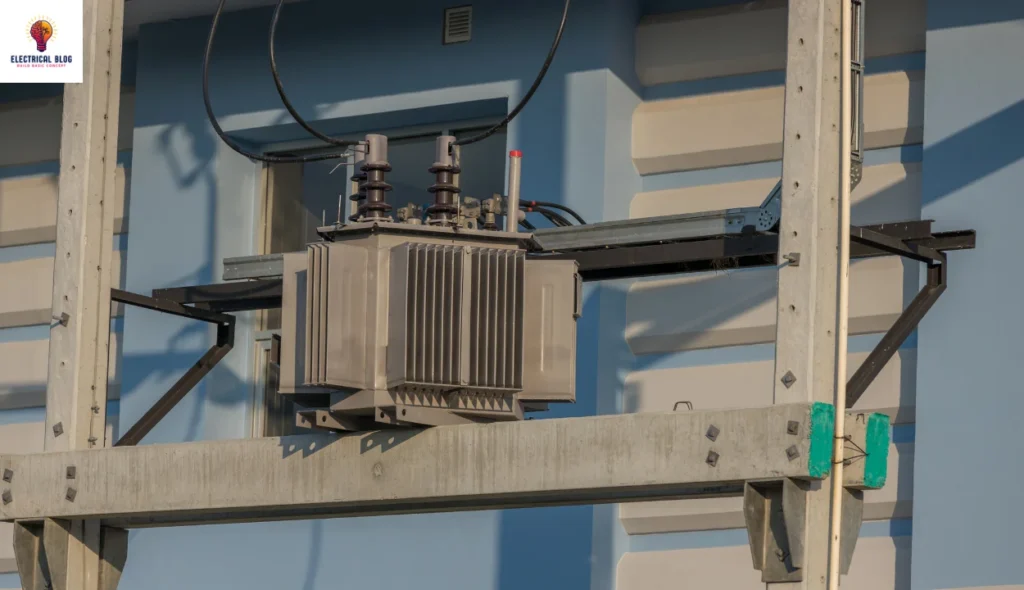
Understanding DP (Distribution Pole) in Electrical Systems
What is DP?
The full form of DP is Distribution Pole, a common term in the electrical field. It is widely used in construction for supporting transformer units. DPs ensure that the electricity supply remains safe and reliable. This structure is designed to handle power flow in a systematic way.
How does DP operate?
Each DP operates through a mechanical setup that may work independently or in a linked system. These panels often include a switch to manage simultaneous connections. Proper mounting is crucial in ensuring DPs can utilize their design for stability. This setup helps ensure a steady power flow in distribution networks.
Importance in Electrical Systems:
The abbreviation DP is related to handling high-voltage supply networks. It offers double protection by improving systematic control over connections. Its structure is built to withstand strong mechanical stress, ensuring safe and stable operations. This feature makes DP essential in modern electrical systems.
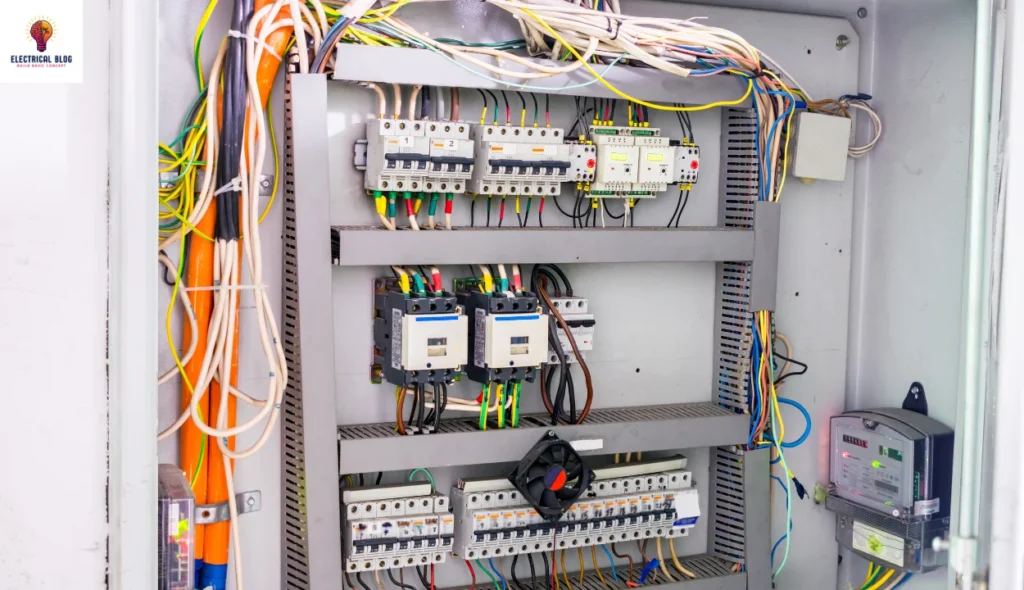
Understanding DP (Double Pole) in electrical systems
What is DP?
The full form of DP is Double Pole, a key term in electrical systems. It refers to switches that control power in circuits. Each DP operates using two separate connections that work independently or together. This design ensures a safe and complete supply flow. You can also read SPDT Switch.
How DP switches work
DP switches are mechanically linked to manage electric flow efficiently. They can control simultaneously or separately to ensure reliable power distribution. These connected systems are common in electrical setups for better control. The system helps prevent overload by operating in staggered steps.
Importance of DP in circuits:
DP switches are designed to contain two control points for improved safety. This ensures power can switch independently or simultaneously in complex systems. Their staggered operation enhances protection in complete electrical networks. DP switches are widely used for stable power control.
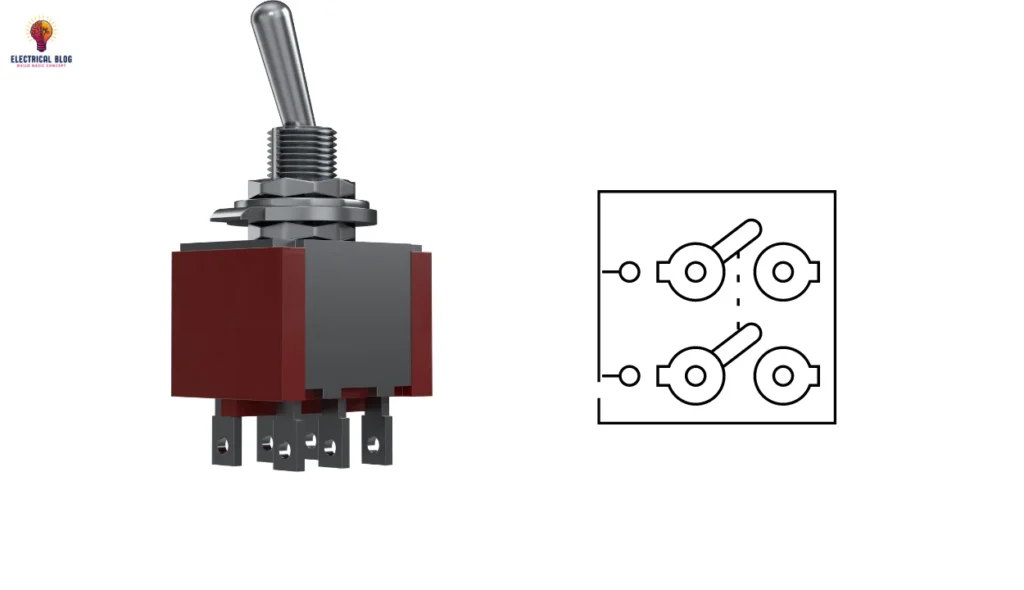
Different Meanings of DP in Electrical Systems
| DP Meaning | Description |
|---|---|
| Distribution Panel | A Distribution Panel is a key component in infrastructure that helps manage power circuits and efficiently distributes electricity across systems. |
| Double Pole | The Double Pole design features a switch that controls two circuits at once. It is often used in automation and substation setups for safe power flow. |
| Direct Print | In electronics, Direct Print technology creates printed boards for flexible and compact applications that improve system efficiency. |
| Data Processing | DP can also refer to Data Processing, commonly seen in automation systems to monitor, manage, and control power usage efficiently. |
| Distribution Point | A Distribution Point is a vital term in infrastructure, where it helps in dividing power across devices using sensors for stable performance. |
Conclusion
In electrical systems, DP can mean different things. It can be a Distribution Panel, Double Pole, Data Processing, or Direct Print. Each interpretation is vital to the electrical industry. It manages power distribution and enables modern automation and circuit design. It’s vital for electrical engineers to know the importance full form of DP in these contexts.
This article is a guide to the meanings of full form of DP. It provides insights into its role in electrical systems. This overview aims to make us the top source on this topic. We want to help professionals and enthusiasts better understand the full form of DP.
Read more: 5 test of current transformer