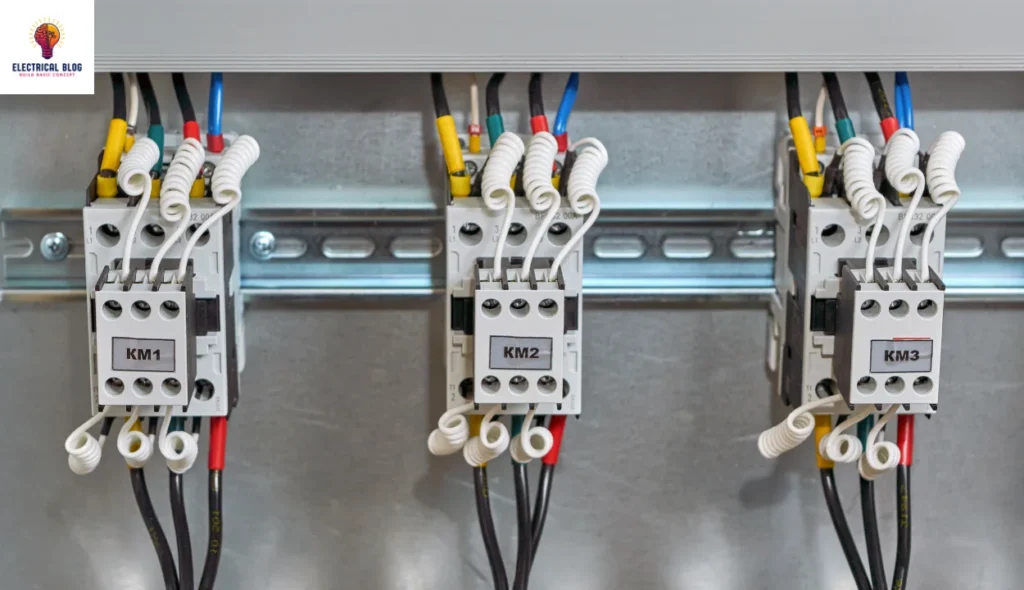
Introduction
A magnetic starter is an essential device used to control the electric motor in various applications. It uses a contactor to manage the current flow and provide the necessary overload protection. With the help of an overload relay, it helps protect the motor from damage by breaking the supply to the circuit if necessary.
In addition to starting, it can also stop and reverse the motor. This makes it an ideal choice for different types of starters, like manual and magnetic starters. The working of a magnetic starter ensures that the motor is efficiently controlled, delivering optimal electrical power for its operation.
What is a magnetic starter?
A magnetic starter is a switch that helps in starting an electric motor with a large load. It works electromagnetically, providing under-voltage protection and overload protection to ensure safety. In case of a power failure, it has an automatic cutoff, offering a safe method for motor control.

How does a magnetic starter work?
The magnetic starter is essential in motor control, offering features like an overload relay, contactor, and digital protective relays. These components work together to protect the motor and ensure safe operation under various conditions. The overload relay and electromagnet help detect issues like power failure, automatically disengaging the motor when needed.
To ensure proper operation, motor control centers often use combination starters along with switchgear and control devices. Fuses, circuit breakers, and disconnecting means are essential for short-circuit protection. Additionally, momentary switches are used to control the motor, with the switch returning to a normal position after being released, making it safer than traditional latching switches.
In complex systems, the motor protection setup includes heaters and starter coils. The motor will only operate when the power is restored, and the contacts are correctly aligned. With the combination of overload and motor protection, these systems provide comprehensive protection and prevent damage to the motor under various working conditions. The control voltage is carefully managed to ensure the motor functions reliably in all scenarios.
Operation of Magnetic Starters
The magnetic starter works by using push switches to control the motor. When the start switch is pressed, the electromagnet in the contactor is energized, which allows the motor to start running. As soon as the start button is released, the magnetic switch remains engaged, maintaining the motor running with self-sustaining current, even without the button being pressed.
If the stop button is pressed, it breaks the circuit, de-energizing the electromagnet in the contactor and cutting off the power to the motor. This stops the motor’s operation. The push-to-make and push-to-break switches ensure safe and reliable motor power control, making the system effective for continuous switching and operation.

Applications of Magnetic Starters
Magnetic starters are commonly used in woodworking machinery, such as cabinet saws and shapers, to handle higher horsepower needs.
For smaller loads, such as a drill press or handheld tools, a standard switch is usually sufficient instead of a magnetic starter.
Many machines come with stock components like magnetic starters, but aftermarket starters are also available for replacement or retrofitting older systems.
Older machines often require replacements or upgrades, and magnetic starters are essential for ensuring they run efficiently.
Magnetic starters can be fitted to various equipment where high-performance machines demand reliable and safe operation.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Magnetic Starters
Advantages:
Overload protection and under-voltage protection help prevent damage to electric motors.
The motor connection is automatically cut off during a power failure, ensuring safety.
Economical and easy to install and maintain, they make a cost-effective choice.
Reversible versions offer flexibility for different motor control needs.
Operating switches allow for controlled and operating motor functions either remotely or locally.
Helps protect against harm caused by inrush currents and voltage drops.
Can be wired flexibly to meet various control necessities, such as flicking and changing motor operations.
Disadvantages:
Limited to 5 HP or below, which may not be sufficient for larger motors.
Motor’s lifespan may be reduced due to the high inrush current.
Potential harm to the windings in the motor and issues with the power line.
Magnetic Starter Vs Contactor
| Feature | Magnetic Starter | Contactor |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Provides a secure technique to start and control the motor. | Primarily an electrically controlled switch. |
| Components | Includes overloads, arc extinguishing devices, and contact systems. | Usually just the contact systems. |
| Operation | Works with an electromagnetically controlled contactor to energize or de-energize the motor. | Electromagnetically controlled but doesn’t handle overload protection. |
| Mounting | Field mounted, often in a front-engine layout. | Typically stationary, fixed in place. |
| Current and Voltage | Rated for motor’s horsepower and current capacity. | Classified mainly by voltage capacity. |
| Overload Protection | Includes overloads to protect the motor. | No overload protection built in. |
| Types | Available in types like auto transformer, star delta starter, etc. | Available in auxiliary, spring-loaded, or movable configurations. |
| Contact Types | Uses NO contacts (normally open) for activation. | Generally uses NO contacts as well, but simpler in design. |
Conclusion
Magnetic starters are essential for controlling and protecting electric motors, offering valuable benefits like overload protection, under-voltage protection, and safe operation during power failures. These starters are economical, easy to maintain, and available in both reversible and irreversible versions for various motor control applications. They ensure the motor’s lifespan by protecting it from issues like high inrush current and voltage drops.
However, they are limited to 5 HP or smaller motors, and using them with larger motors can lead to reduced performance or harm to the motor’s windings. Despite these drawbacks, magnetic starters are widely used for electric motors, providing a reliable and efficient solution for both local and remote motor control.