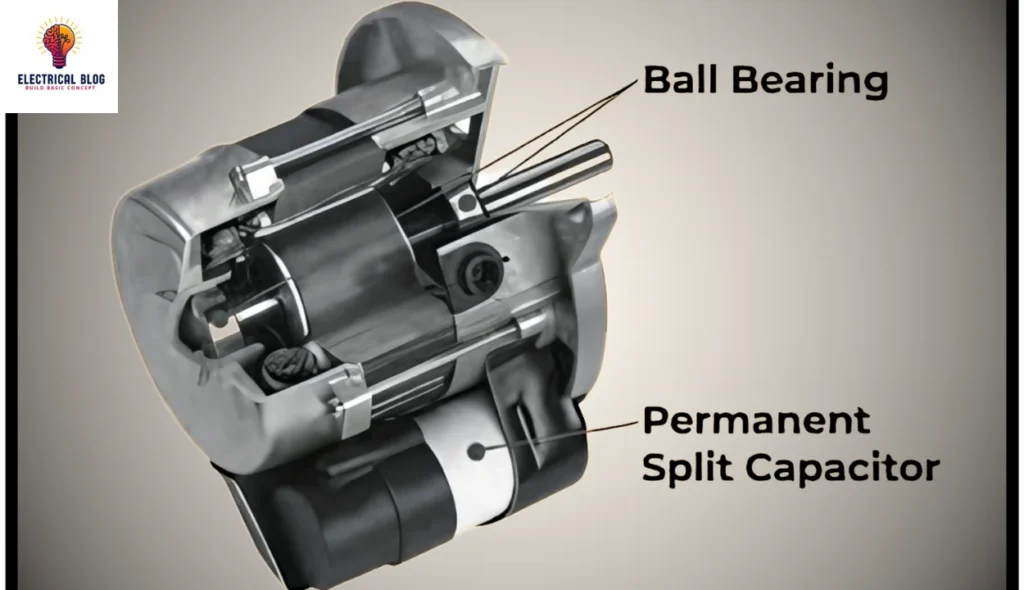
Introduction
The Permanent Split Capacitor Motor (PSC) is widely used in household and industrial devices due to its reliable performance. It features a cage rotor with main and auxiliary windings that are connected in series. A capacitor remains permanently linked in the circuit, ensuring smooth starting and running across all phases. This self-starting design effectively powers various appliances with minimal limitations.
The PSCM offers several advantages, such as stable electromagnetic field generation and reduced maintenance. Its working mechanism efficiently generates a rotating force using a single-value capacitor for seamless operation. With versatile applications, the component is ideal for systems requiring constant run performance. By combining simplicity and efficiency, the Permanent Split Capacitor Motor is a dependable solution for various needs.
What is a Permanent Split Capacitor motor?
The Permanent Split Capacitor Motor (PSCM) is a single-phase induction motor designed for improved performance and efficiency. It features two windings on the stator: a main or running winding and an auxiliary or starting winding. A capacitor is connected between the starting winding and the power supply, ensuring smooth startup and stable operation during continuous use.
Unlike other motors, the PSCM has one capacitor that stays connected throughout starting and running. Its design includes a squirrel cage rotor, common in split-capacitor systems, which enhances stability. This unique setup makes the PSCM ideal for applications requiring consistent run conditions and minimal maintenance.
Permanent Split Capacitor Moter diagram
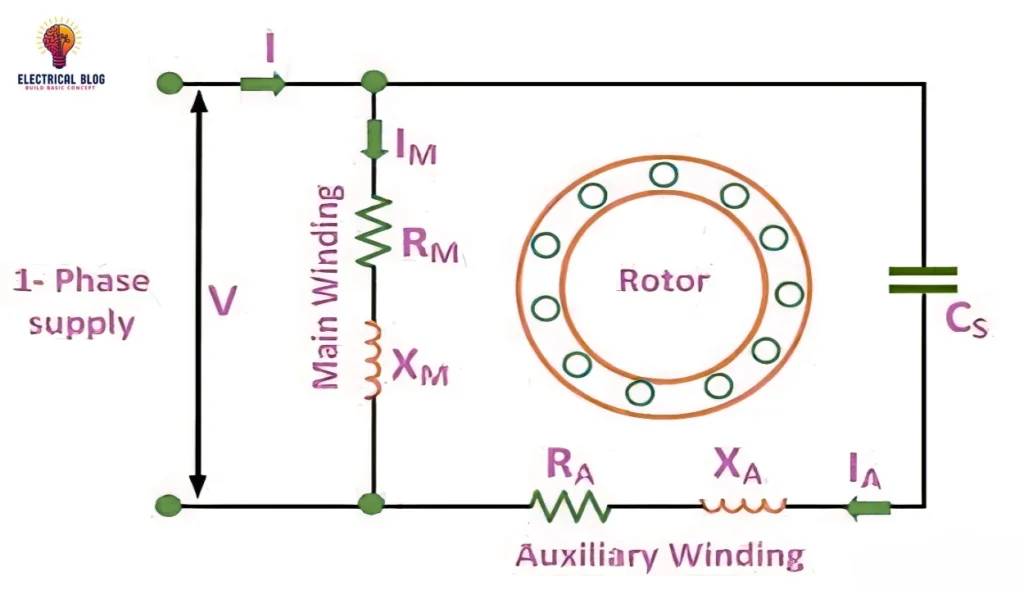
Working of Permanent Split Capacitor Motors
The Permanent Split Capacitor (PSC) motor is a single-phase induction motor that efficiently operates on a unique design. It comprises two windings, the main (or running) and the auxiliary, both connected in series to form a balanced circuit. A capacitor is permanently connected in this circuit, ensuring a stable magnetic field for smooth operation.
This operating method relies on a principle in which the capacitor creates a phase shift, producing a two-phase effect in the stator. As a result, the rotor, typically a squirrel cage type, effectively generates torque for self-starting. This method eliminates the need for a centrifugal switch, making it less noisy and more efficient.
The PSC motor’s single-value capacitor remains active during both starting and running, enhancing performance. This reliable setup, often referred to as a split-capacitor system, ensures uniform operation and enables the motor to produce steady current under various phases and load conditions.
Permanent Split Capacitor Motor Efficiency
The Permanent Split Capacitor Motor is a preferred choice for energy-conscious applications due to its minimal loss. Its continuous connection with the capacitor ensures stable efficiency, making it a key selling point for split-motor designs.
Characteristics of Permanent Split Capacitor Motors
The Permanent Split Capacitor Motor is self-starting and effectively handles inertia, making it suitable for applications requiring stable performance.
It achieves a power factor of 0.8 or above, ensuring improved efficiency while maintaining consistent operation.
This motor delivers moderately strong starting torque, which is ideal for systems with medium to high load requirements.
The PSC motor efficiently generates and maintains speed even under fluctuating conditions, ensuring a steady output.
It can handle variations in load, ranging from 75% to 85%, without major performance issues.
By achieving uniform performance, the motor maintains constant output, providing reliable performance in demanding systems.

Types of Permanent Split Capacitor Motors
The Permanent Split Capacitor Motor (PSC) has two common types based on starting torque and application needs. The first type features low starting torque, ideal for fans, blowers, and light-duty pumps that require constant speed with minimal performance variation.
The second type is designed for higher starting torque, making it suitable for demanding systems like compressors, refrigeration units, and heavy loads. These motors perform steadily during continuous operations. This ensures they are efficient and deliver reliable power over time.
Advantages of Permanent Split Capacitor Motors
The Permanent Split Capacitor Motor has a simple design with fewer parts, reducing maintenance needs.
It operates quietly and smoothly, making it ideal for applications that require less noise.
Its robust build ensures durable performance, enhancing its lifespan in demanding duty cycles.
The PSC motor is highly efficient, consumes less energy, and offers superior performance in continuous operations.
It delivers stable power and maintains a balanced magnetic field, similar to polyphase motors.
Unlike split-phase motors, the PSC motor avoids frequent stops and starts, improving mechanical wear resistance.
With no centrifugal switch, the PSC motor is reliable for higher ratings and involved tasks.
The motor’s steady torque output makes it suitable for various applications, ensuring effective performance throughout its use.
Limitations of Permanent Split Capacitor Motors
The Permanent Split Capacitor Motor is generally more expensive due to its higher costs of capacitors and components.
It has limited capabilities in providing torque, making it less suitable for applications that require high starting power.
The motor’s winding remains energized during operation, which can lead to increased losses and overheating.
PSC motors are bulkier in size compared to other single-phase motors, limiting their use in compact systems.
These motors are often sensitive to voltage fluctuations, requiring stable input power for optimal performance.
PSC motors provide fixed speed with minimal control options, making them unsuitable for tasks needing precise regulation.
They are prone to oil leakage and paper insulation damage, reducing their durability in demanding environments.
Applications of Permanent Split Capacitor Motors
The Permanent Split Capacitor Motor is widely used in HVAC systems, such as air conditioners and ventilation systems, due to its quiet and efficient operation.
It is ideal for driving fans, blowers, and pumps, ensuring reliable performance in various environments.
This motor is commonly found in office equipment, like copiers, where stable and quiet operation is crucial.
In water and oil machinery, the PSC motor proves suitable for continuous tasks requiring steady power.
Conclusion
The Permanent Split Capacitor Motor is a reliable variant of single-phase induction motors, known for its constant-speed performance. Its permanent capacitor design provides stable torque. This makes it perfect for both consumer and industrial uses that need consistent output.
This motor delivers superior capability in powering various products and processes. Even with some limits, its better starting and controls make it a strong choice for different systems needing accurate speed management.