Introduction
In my years of working with electrical circuits, I’ve often seen how crucial a ballast resistor is in ensuring a stable flow of current despite variations in voltage. This essential device is widely used in automotive ignition systems and fluorescent lamps, where it compensates for negative volt-ampere characteristics and prevents damage caused by sudden spikes. The unique property of a ballast resistor is its ability to adjust resistance dynamically—it increases when the temperature rises and decreases when the current flow drops, allowing for efficient energy regulation.
Made from a special resistive material, this component is vital in ensuring that the circuit remains stable and works optimally. Whether in high-powered lamps or an ignition system, its action is crucial for maintaining performance. The ballast resistor shows how electrical parts can self-regulate. Its smart design proves its effectiveness.
What is a ballast resistor?
A ballast resistor is an essential electronic component that helps regulate the current flowing in an electrical circuit by adjusting its resistance. Unlike a fixed load, its value varies, adapting to changes in the system. This function is crucial in ignition systems, where it controls the voltage to the ignition coil, preventing overcurrent faults and ensuring stable operation. Made from different materials such as carbon, metal film, and ceramic, these resistors come in various designs, including wire-wound types. Their construction allows them to withstand high temperatures and provide stability in sensitive circuits.
In fluorescent lamps and electronic ballasts, these resistors help manage power dissipation and prevent sudden surges that could shorten the life of the devices. Their composition and ohm range can vary from a few to a hundred ohms, depending on the application. Unlike standard resistors, they do not simply dissipate power; instead, they actively limit excess energy to protect the system. Their ability to adapt to changes in voltage and load makes them vital in both automotive and industrial systems. By reducing stress on key components, ballast resistors help prolong the engine’s efficiency and durability. You can also read variable resistors.
What does a ballast resistor do?
A ballast resistor helps maintain stability in an electrical circuit by controlling the current flowing through it. When the temperature rises, its resistance increases, which helps limit excess power and protect other components from damage. In automotive applications, it prevents voltage drain from the battery when the starter motor starts the engine. It is also widely used in lighting, such as fluorescent lamps, LEDs, and neon lights, to regulate power. By adjusting to changes, the resistor ensures efficiency and prolongs the lifespan of connected devices. You can also read neutral earthing resistors.
Applications of a ballast resistor
A ballast resistor is essential in automotive and lighting applications, helping to regulate voltage and current in an electrical system. It prevents overcurrent and overvoltage events, protecting sensitive equipment from damage. This makes it a crucial component in stable power management across various applications.
Ballast Resistor for Automotive Applications
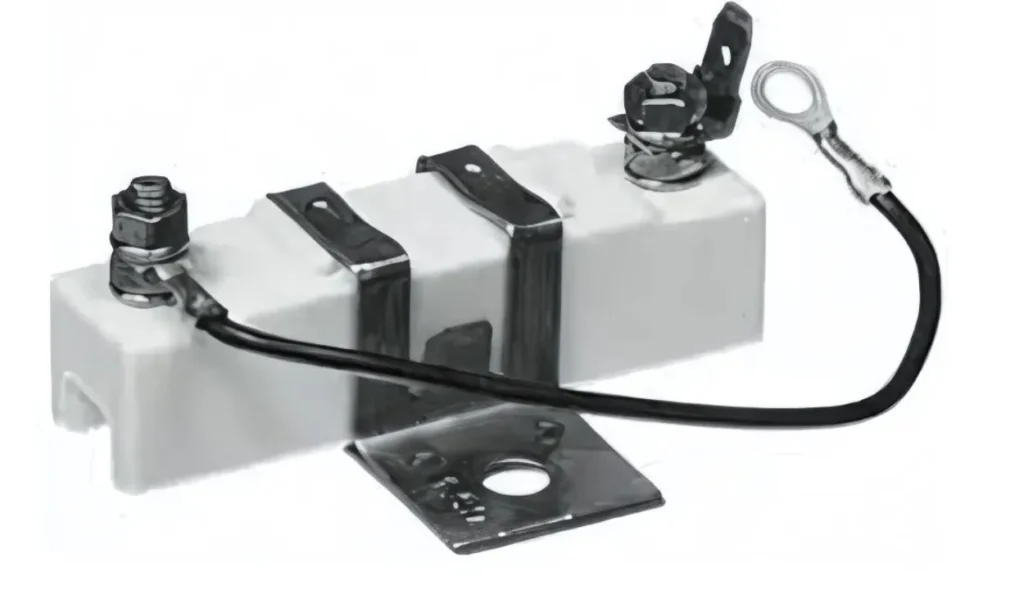
In a car engine, an ignition ballast resistor is placed between the primary source and the coil stud to manage voltage and current flow. When the starter motor cranks, it helps prevent failure by reducing excess power. A jumper wire is connected to supply the required high voltage for ignition. By limiting temperature rise, it ensures long coil life and prevents damage to the ignition system. This resistor plays a vital role in stabilizing power and reducing risk in automotive applications.
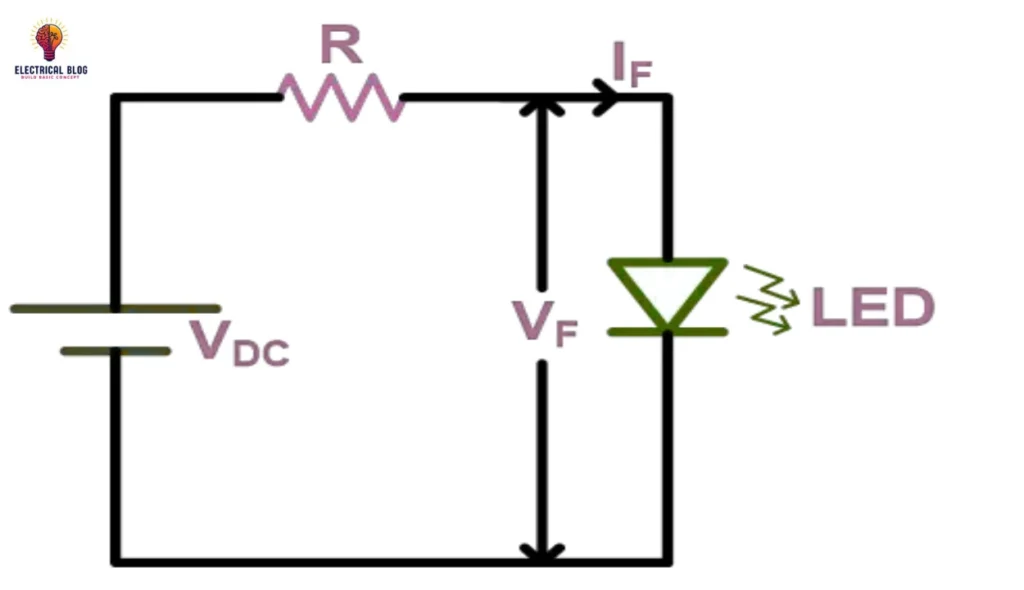
Ballast resistor in an LED circuit
A ballast resistor is used in series with an LED to reduce the voltage and prevent damage. If the supply source is higher than the rated voltage, you cannot connect the LED directly without a resistor. Using the equation, R = (E – VF) / IF, we can determine the correct resistance value. For a 5V DC source, an LED with a 3.1V forward voltage and 9mA current requires a 211Ω resistor. This helps maintain stable current flow and protects the circuit in various conditions.
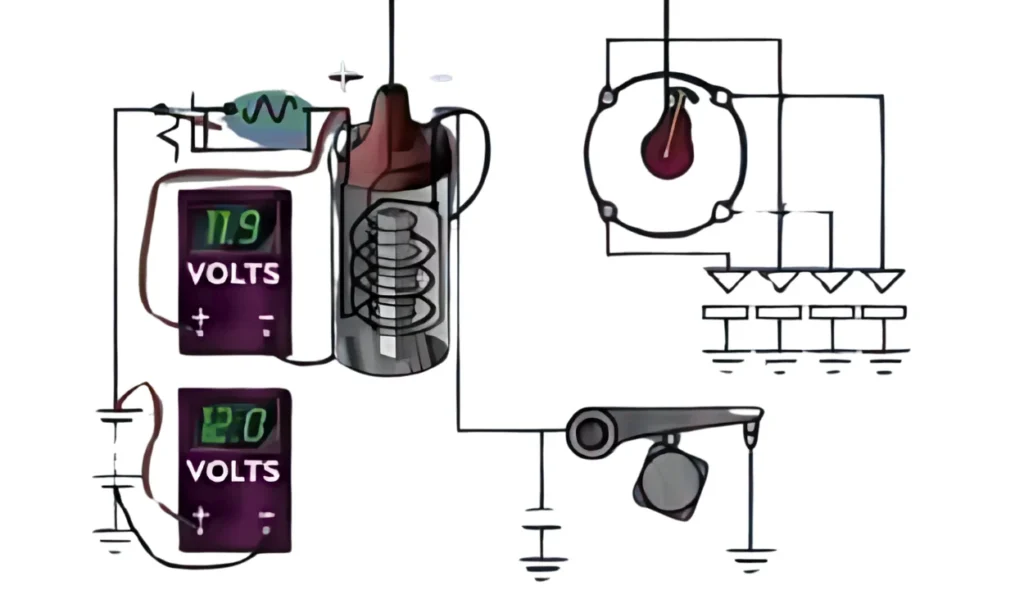
How to Test a Ballast Resistor
To test a ballast resistor, first check the voltage level across the ignition coil using a multimeter or ohmmeter. If the resistor is in good condition, it should reduce the voltage to 7-8V when connected to the ignition system. A faulty resistor may show a high voltage, indicating it is damaged and needs replacement. The resistance can also be measured against its rated value to ensure it functions properly. In automotive applications, the battery usually supplies 12V or 24V, and the ballast helps fulfill the need for regulated power to increase the life of the ignition system. If the voltage remains at the full supply level, the resistor is faulty and must be replaced. You can also read potentiometer.
Types of Ballast Resistors
Fixed Ballast Resistors
A fixed ballast resistor is designed to provide a constant resistance in circuits where a high value is preferred. It is commonly used in applications such as neon lamps, LED circuits, and variable-speed fans. In a fan, the selector switch sets different speed levels using center taps. This allows the speed to adjust smoothly as the resistance varies. The resistor plays a key role in maintaining stability and helping to control power flow in electrical systems.
Self-variable Ballast Resistor
A self-variable ballast resistor adjusts its resistance based on the current flowing through it. As the current increases, the temperature rises, causing the resistance to go up, which helps control the voltage drop. This type of resistor is commonly used in incandescent lamps, where it prevents sudden surges and maintains stability. When the current decreases, the ballast cools down, and the resistance lowers again. It is also used to protect electrical equipment from overcurrent, ensuring safe circuit operation.
Advantages of ballast resistors
A ballast resistor helps regulate voltage and current in electrical systems, ensuring smooth operation and preventing sudden variations.
It acts as a safeguard by offering protection against overvoltage and overcurrent, preventing damage to sensitive equipment.
These resistors are widely utilized in automotive and lighting circuits, where they provide stability and prevent power fluctuations.
By being strategically applied in circuits, they help diminish excess power and improve the overall efficiency of electrical regulation.
Other applications of ballast resistors
Ballast resistors are commonly used in automotive circuits to help with ignition by controlling the current in the primary winding of the coil.
In LED circuits and fluorescent lamps, they help regulate voltage to prevent sudden fluctuations and extend component life.
These resistors are used in vapor lamps and laser circuits, such as HeNe tubes, to compensate for changes in line voltage.
A 75 KΩ ballast resistor is typically found in HeNe lasers, where it assists in restricting the tube current for stability.
They are widely used in low-power devices, including neon lamps, to control resistance and prevent excess drainage of power.
In simple circuits, these resistors are used to handle low loads while maintaining efficient electrical system performance.
Battery-operated systems use ballast resistors to prevent overloads and reduce unnecessary drainage of energy.
Their role in series circuits ensures the regulation of power distribution while protecting sensitive devices from excessive voltage surges.
Conclusion
A ballast resistor is key in cars and electrical systems. It controls voltage, limits current, and protects delicate devices from too much voltage or current. It is crucial for ignition systems, lighting circuits, and power regulation. It keeps stability and cuts down fluctuations. Different types of ballast resistors are used for specific needs. Fixed and self-variable types help LEDs, fluorescent lamps, vapor lamps, and ignition coils work better. Testing with an ohmmeter or multimeter checks their condition. This helps prevent damage and extends the life of connected systems. Knowing why ballast resistors matter helps you pick the right one for different uses. This choice keeps circuits safe and efficient.