Introduction
Single-phase motors are a type of AC motor that operates on a single-phase power supply. These motors are famous for their simple design. So, they are widely used in many industries and homes. Single-phase motors are preferred for small machines, like appliances, fans, and pumps. Three-phase motors are better for large industrial uses. They are more powerful than two-phase motors. This adaptability makes them invaluable in modern homes. There, reliability, low maintenance, and ease of use are crucial.
Single-phase induction motors power small machine tools and equipment in modern industries. They are used where high power is not needed. They are also used in homes and businesses. They are cheap and small. They are widely used where three-phase power is unavailable or impractical. This increases their importance across sectors.
This article aims to explore single-phase motors. It will cover their principles, applications, and benefits. It will also explain their importance to households and small industries. Knowing their strengths helps readers appreciate their role in today’s electrical systems.
What is a single-phase motor?
An electric motor that runs on a single-phase power source is known as a single-phase motor. It is popular in homes and small businesses. Its use is due to its simplicity and effectiveness. These motors usually have two terminals. They need a capacitor or extra winding to start. So, they are good for low-power uses, like fans, pumps, and small machines.
General Characteristics:
Power Ratings: Common sizes are 1hp, 2hp, 3hp, 5hp, and 10hp motors. They are versatile for many tasks.
Starting torque: Single-phase motors have lower starting torque than three-phase ones. This makes them less efficient for high-load applications.
Construction: For the same power rating, they are larger and heavier than three-phase motors. They must handle higher currents to produce equivalent power.
Differences Between Single-Phase and Three-Phase Motors
The main differences between single-phase and three-phase motors include:
Power Supply:
Single-phase motors run on a single-phase supply. Three-phase motors use a three-phase supply, which is more efficient for high-power applications.
Starting Torque:
Single-phase motors have low starting torque. They are not good for applications needing high initial power.
Size and Weight:
For similar power ratings, single-phase motors are usually larger. They need extra parts to manage the starting process.
Applications:
Single-phase motors are mainly for homes. They power small pumps, fans, and appliances. Three-phase motors are better for high power and efficient industrial use.
In summary, single-phase motors are vital for everyday tasks. Commonly used power ratings are 3hp, 2hp, 5hp, and 10hp. Their traits and limits, compared to three-phase motors, show they work best in low-power situations.
Types of Single-Phase Motors
Single-phase motors are widely used for their simplicity and efficiency. Here are the main types of single-phase motors:
Split-Phase Induction Motor
The split phase induction motor is one of the most widely used types. It operates by using two windings: a starting winding and a running winding. The windings create a phase difference. This allows the motor to start and develop torque. This motor has a low starting current and moderate starting torque. So, it suits small devices like fans and pumps.
Capacitor-Start Induction Motor
The capacitor-start induction motor incorporates a capacitor in series with the starting winding. This design boosts the starting torque. It lets the motor handle heavier loads at startup. A centrifugal switch disconnects the capacitor when the motor reaches a specific speed. These motors are common in applications needing high starting torque. Examples include compressors and air conditioners.
Capacitor-Run Induction Motor
In a capacitor-run induction motor, the capacitor stays in the circuit while the motor runs. This configuration improves efficiency and provides smoother operation. These motors are ideal for continuous operation, such as in fans and small machines. The inclusion of the capacitor allows for better power factor correction.
Shaded Pole Motor
The shaded pole motor has a simple design. A shaded part of the pole creates a rotating magnetic field. It has low starting torque and efficiency. However, it is inexpensive. Therefore, it is often used in low-power applications like small fans, blowers, and toys. These motors are popular. They are reliable and easy to use in low-power situations.
Each type of single-phase motor has unique traits. They suit different applications. Understanding these differences can help in selecting the right motor for specific tasks.
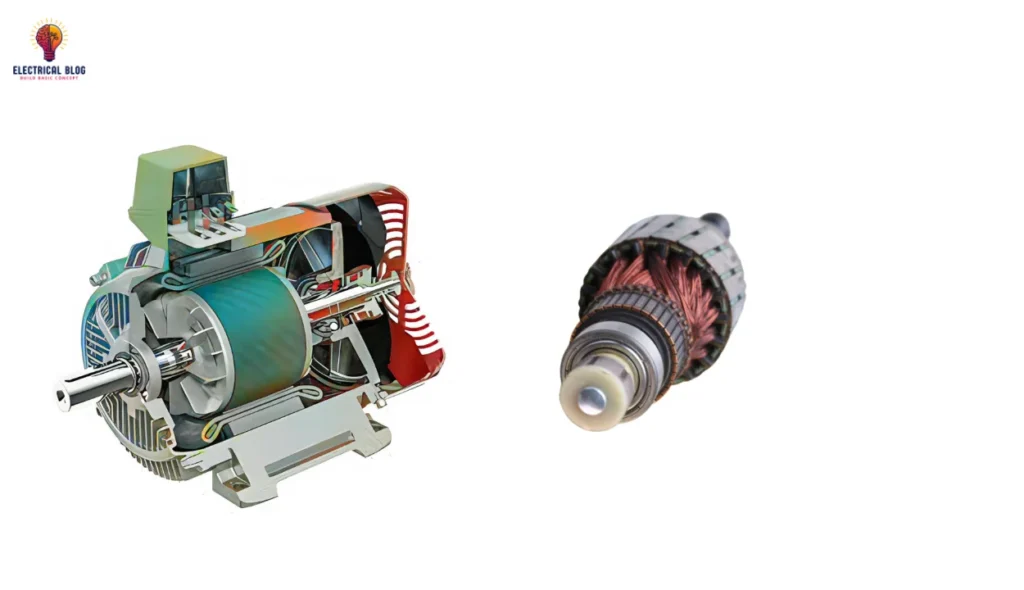

Working Principle of a Single-Phase Motor
Single-phase motors use electromagnetic induction. They have a stator and rotor that generate rotational energy. The stator has a single-phase winding. It creates a magnetic field when current flows through it. Unlike three-phase motors, a single-phase motor does not create a rotating magnetic field. It generates a pulsating magnetic field that peaks at 0° and 180° electrical. The rotor experiences currents as a result of this pulsing field. These interact with the magnetic field to create torque and start rotation.
For the motor to function, the interaction between the rotor and stator is essential. A current is induced in the rotor when the magnetic field of the stator varies. This induced current creates a magnetic field. It generates torque by interacting with the stator field. A magnetic force drives the rotor to rotate. It continues as long as the stator current is applied.
Starting single-phase motors can be tough. They lack a rotating magnetic field. To boost starting torque, various designs are used, like capacitor-start or split-phase motors. In a capacitor-start motor, a capacitor is briefly connected to the starting winding. This boosts the starting torque significantly. However, once the motor reaches a specific speed, the capacitor disconnects to avoid power loss. Despite their advantages, single-phase motors have drawbacks. They can overheat and have low starting torque. So, they are less suited for high-load applications than three-phase motors.
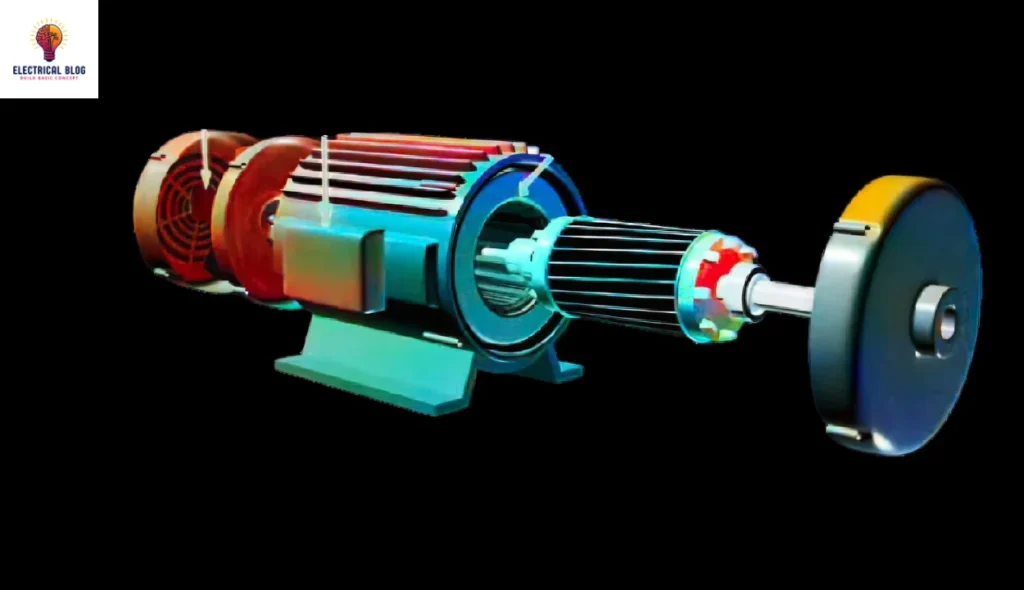
Construction and Components
Stator
The stationary component of a single-phase motor is called the stator. It has a laminated steel core and winding coils. The coils produce a magnetic field when they are powered. Single-phase induction motors have two main stator windings: the main and the auxiliary. These windings create a phase difference, which is crucial for starting the motor. AC flowing through the stator windings creates a pulsating magnetic field. It interacts with the rotor, enabling the motor to work.
Rotor
The revolving part inside the stator is called the rotor. Single-phase motors often use a squirrel cage design. It allows for efficient, loaded operation. The stator’s magnetic field induces a current in the rotor bars. This creates an opposing magnetic field that generates torque. This interaction between the stator and rotor is what drives the motor’s rotation. However, single-phase motors are not self-starting. They need extra mechanisms to start.
Capacitors (if applicable)
Some single-phase motors use capacitors to improve starting torque and efficiency. In a capacitor-start motor, a capacitor is in series with the auxiliary winding. This setup shifts the phase of the current in the auxiliary winding. It creates a better magnetic field that helps the motor start. The circuit usually disconnects the capacitor once the motor reaches a set speed. This allows the motor to run only on the main winding.
Auxiliary Winding
The auxiliary winding is vital in single-phase motors. It provides the initial torque to start the rotor. This winding is at an angle to the main winding. It creates the required phase difference. In capacitor-start motors, the auxiliary winding connects to a capacitor. This boosts its ability to generate startup torque. The auxiliary winding’s design affects the motor’s performance and efficiency.
Applications of Single-Phase Motors
Single-phase motors are versatile and widely used. They are straightforward, effective, and simple to use. Here’s a detailed look at their primary applications:
Household Appliances
Single-phase motors are prevalent in household appliances. They power devices like fans, washing machines, and air conditioners. They also power refrigerators and vacuum cleaners. Their simple design allows them to run on standard household voltage. So, they are ideal for everyday use. Their reliability and low maintenance make these motors popular in homes.
Light Industrial Machinery
In light industrial settings, single-phase motors power small machines and tools. They are used in equipment that needs moderate horsepower. This includes small machine tools, conveyor systems, and agricultural machines. Their efficiency makes them suitable for tasks that don’t need heavy power. They allow for smoother operations in assembly lines and light manufacturing.
HVAC Systems
Another significant application of single-phase motors is in HVAC systems. These motors drive parts like compressors and blowers. They provide vital airflow and temperature control in buildings. They can handle variable loads. So, they are vital for efficiently maintaining comfortable indoor spaces.
In summary, single-phase motors are vital in homes and industries. They power household appliances, light machinery, and HVAC systems. They ensure efficient operation across various sectors.
Advantages of Single-Phase Motors
Single-phase motors are widely used, especially in homes and light industry. Several significant benefits are responsible for their popularity:
Simplicity in Design and Installation
Single-phase motors feature a straightforward design that simplifies both manufacturing and installation. They typically consist of fewer components than three-phase motors, making them easier to assemble. This simplicity reduces the chances of failure and makes maintenance easier. Also, the installation process is easier. These motors can run on standard household electricity. They need no special wiring or circuitry.
Cost-effectiveness
One of the standout advantages of single-phase motors is their cost-effectiveness. They are cheaper to make than other motors, like three-phase ones. Their design uses cheaper conductors and core materials. This makes them ideal for low-power applications. As a result, consumers can enjoy reliable, low-cost performance. Small businesses and people particularly benefit from this.
Versatility in Smaller Loads
Single-phase motors are very versatile. They suit many small loads. They power many household appliances, like fans, fridges, and washers. They also power light industrial equipment. Their versatility lets them cater to diverse uses. They work well in places where heavy-duty motors are not needed.
In conclusion, single-phase motors are popular in many sectors. Their simple design and low cost make them a top choice. They are easy to install and can handle small loads. Their unique advantages make them reliable and efficient. So, they are essential in everyday machinery.
Common Problems and Troubleshooting of Single-Phase Motors
Single-phase motors are widely used. But, they can have common problems that affect their performance and reliability. Here are a few common problems and solutions.
Overheating
Overheating is a common issue with single-phase motors. It can be due to overloading, poor ventilation, or electrical faults. When a motor runs beyond its rated capacity, it overheats. This can damage the insulation and lower efficiency. To troubleshoot, ensure the motor is not overloaded. Also, it must have enough airflow around it. Check for dust or debris that may block airflow. This can help prevent overheating. Additionally, monitoring operating temperatures can alert you to potential issues before they escalate.
Starting Issues
Starting issues can show as a failure to start or a loss of operation after starting. This problem may be due to faulty capacitors, a bad switch, or low power. A common cause is capacitor failure. If the capacitor is faulty, the motor may not generate enough starting torque. To troubleshoot, inspect the capacitor for signs of damage or test it with a multimeter. Also, check the power supply. The voltage must be acceptable, and there must be no loose connections.
Motor noise and vibrations
Motor noise and vibrations can signal issues with its components. These include bearings, misalignment, and loose parts. Excessive vibration may cause mechanical problems. It can wear bearings or even fail the motor. To troubleshoot, listen for unusual sounds. Grinding, screeching, or buzzing may signal a fault. Check the motor for loose or worn parts. Also, ensure it is aligned with the driven load. Addressing these issues promptly can enhance the longevity and performance of the motor.
Fixing three issues can greatly boost your single-phase motor’s reliability and efficiency. They are overheating, starting problems, and noisy vibrations.
Maintenance Tips for Single-Phase Motors
Regular maintenance is crucial. It ensures single-phase motors run well and last long. Proper maintenance can prevent breakdowns and extend the motor’s life. Here are some essential maintenance tips:
Regular Cleaning and Inspection
Routine cleaning and inspection of the motor are vital to maintaining its efficiency. Dust and dirt can accumulate on the motor’s exterior. This affects ventilation and can cause overheating. Regularly remove contaminants from the motor’s surface. Pay special attention to the fan cover and ventilation openings. This will promote airflow. Also, check the motor for wear or damage, such as frayed wires or cracks in the housing. Conducting these checks regularly can help identify potential issues before they escalate.
Checking motor connections and capacitors
Ensuring proper electrical connections is essential for the efficient operation of single-phase motors. Regularly check motor connections and capacitors to ensure they are secure and free from corrosion. Loose or damaged connections can lead to voltage drops and operational failures. Check capacitors for bulging or leakage. Faulty ones can cause starting issues or prevent the motor from running. Testing the electrical connections with a multimeter can help. It can find any irregularities.
Lubrication Guidelines
Proper lubrication is essential for reducing friction and wear on motor components. Follow the manufacturer’s advice on what lubricant to use and how often to apply it. Grease all lubrication points. Check them for leaks and low oil. Avoid over-lubricating, as excess grease can lead to overheating and other issues. Regularly checking and replacing lubricants can improve the motor’s performance and lifespan.
These maintenance tips will ensure your single-phase motor’s reliability and longevity. The tips are: 1. Clean and inspect regularly. 2. Check motor connections and capacitors. 3. Follow lubrication guidelines.
Conclusion
Single-phase motors are vital in our daily lives. They reliably power many household and industrial devices. Their simple design and ease of use suit them for low-power tasks. Single-phase motors are vital in our daily lives. They run fans, blowers, pumps, and small appliances. They are preferred where power demand is low. They are a cost-effective choice for many users. They are perfect for small enterprises and homes. They can run efficiently with less electrical infrastructure.
When choosing the right type of single-phase motor, several factors should be considered. Understanding the particular application needs is crucial. This includes the required torque, speed, and starting characteristics. Different single-phase induction motors suit different tasks. Shaded-pole motors are best for low-power jobs. Capacitor-start motors provide high starting torque for tougher tasks. Choosing the right motor boosts performance and saves energy. It cuts costs over time. These factors will help ensure the motor meets both performance and budget needs.
Read more: Permanent Split Capacitor Moter